Increased hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity and hepatic insulin resistance in low-birth-weight rats
- PMID: 17895287
- PMCID: PMC2761595
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00356.2007
Increased hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity and hepatic insulin resistance in low-birth-weight rats
Abstract
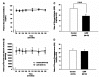
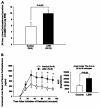
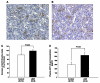
Individuals born with a low birth weight (LBW) have an increased prevalence of type 2 diabetes, but the mechanisms responsible for this association are unknown. Given the important role of insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes, we examined insulin sensitivity in a rat model of LBW due to intrauterine fetal stress. During the last 7 days of gestation, rat dams were treated with dexamethasone and insulin sensitivity was assessed in the LBW offspring by a hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp. The LBW group had liver-specific insulin resistance associated with increased levels of PEPCK expression. These changes were associated with pituitary hyperplasia of the ACTH-secreting cells, increased morning plasma ACTH concentrations, elevated corticosterone secretion during restraint stress, and an approximately 70% increase in 24-h urine corticosterone excretion. These data support the hypothesis that prenatal stress can result in chronic hyperactivity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, resulting in increased plasma corticosterone concentrations, upregulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis, and hepatic insulin resistance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Treatment with an SSRI antidepressant restores hippocampo-hypothalamic corticosteroid feedback and reverses insulin resistance in low-birth-weight rats.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010 May;298(5):E920-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00606.2009. Epub 2010 Jan 26. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20103738 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperactivation of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis in streptozotocin-diabetes is associated with reduced stress responsiveness and decreased pituitary and adrenal sensitivity.Endocrinology. 2002 May;143(5):1761-8. doi: 10.1210/endo.143.5.8809. Endocrinology. 2002. PMID: 11956158
-
Effect of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis alterations on glucose and lipid metabolism in diabetic rats.Genet Mol Res. 2015 Aug 14;14(3):9562-70. doi: 10.4238/2015.August.14.19. Genet Mol Res. 2015. PMID: 26345889
-
Glucose homeostasis and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis during development in rats.Am J Physiol. 1990 Nov;259(5 Pt 1):E601-13. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.259.5.E601. Am J Physiol. 1990. PMID: 2240199 Review.
-
Excessive portal venous supply of long-chain free fatty acids to the liver, leading to hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal-axis and sympathetic activation as a key to the development of syndrome X. A proposed concept for the induction of syndrome X.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999 Nov 18;892:308-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb07804.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999. PMID: 10842671 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Disassociation of liver and muscle insulin resistance from ectopic lipid accumulation in low-birth-weight individuals.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Dec;96(12):3873-80. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-1747. Epub 2011 Oct 12. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011. PMID: 21994962 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental origins of obesity and type 2 diabetes: molecular aspects and role of chemicals.Environ Health Prev Med. 2013 May;18(3):185-97. doi: 10.1007/s12199-013-0328-8. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Environ Health Prev Med. 2013. PMID: 23382021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dexamethasone enhances oxidative stress-induced cell death in murine neural stem cells.Neurotox Res. 2012 Aug;22(2):127-37. doi: 10.1007/s12640-012-9308-9. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Neurotox Res. 2012. PMID: 22237944
-
Early metabolic defects in dexamethasone-exposed and undernourished intrauterine growth restricted rats.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50131. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050131. Epub 2012 Nov 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23166830 Free PMC article.
-
Stress, Sex, and Sugar: Glucocorticoids and Sex-Steroid Crosstalk in the Sex-Specific Misprogramming of Metabolism.J Endocr Soc. 2020 Jul 3;4(8):bvaa087. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvaa087. eCollection 2020 Aug 1. J Endocr Soc. 2020. PMID: 32734132 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barthel A, Schmoll D. Novel concepts in insulin regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2003;285:E685–E692. - PubMed
-
- Carlsson S, Persson PG, Alvarsson M, Efendic S, Norman A, Svanstrom L, Ostenson CG, Grill V. Low birth weight, family history of diabetes, and glucose intolerance in Swedish middle-aged men. Diabetes Care. 1999;22:1043–1047. - PubMed
-
- Chiasson JL, Liljenquist JE, Finger FE, Lacy WW. Differential sensitivity of glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis to insulin infusions in dogs. Diabetes. 1976;25:283–291. - PubMed
-
- Clark PM. Programming of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis and the fetal origins of adult disease hypothesis. Eur J Pediatr. 1998;157(Suppl 1):S7–S10. - PubMed

