Antagonistic bacterial interactions help shape host-symbiont dynamics within the fungus-growing ant-microbe mutualism
- PMID: 17896000
- PMCID: PMC1978530
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000960
Antagonistic bacterial interactions help shape host-symbiont dynamics within the fungus-growing ant-microbe mutualism
Abstract
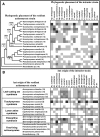
Conflict within mutually beneficial associations is predicted to destabilize relationships, and theoretical and empirical work exploring this has provided significant insight into the dynamics of cooperative interactions. Within mutualistic associations, the expression and regulation of conflict is likely more complex than in intraspecific cooperative relationship, because of the potential presence of: i) multiple genotypes of microbial species associated with individual hosts, ii) multiple species of symbiotic lineages forming cooperative partner pairings, and iii) additional symbiont lineages. Here we explore complexity of conflict expression within the ancient and coevolved mutualistic association between attine ants, their fungal cultivar, and actinomycetous bacteria (Pseudonocardia). Specifically, we examine conflict between the ants and their Pseudonocardia symbionts maintained to derive antibiotics against parasitic microfungi (Escovopsis) infecting the ants' fungus garden. Symbiont assays pairing isolates of Pseudonocardia spp. associated with fungus-growing ants spanning the phylogenetic diversity of the mutualism revealed that antagonism between strains is common. In contrast, antagonism was substantially less common between more closely related bacteria associated with Acromyrmex leaf-cutting ants. In both experiments, the observed variation in antagonism across pairings was primarily due to the inhibitory capabilities and susceptibility of individual strains, but also the phylogenetic relationships between the ant host of the symbionts, as well as the pair-wise genetic distances between strains. The presence of antagonism throughout the phylogenetic diversity of Pseudonocardia symbionts indicates that these reactions likely have shaped the symbiosis from its origin. Antagonism is expected to prevent novel strains from invading colonies, enforcing single-strain rearing within individual ant colonies. While this may align ant-actinomycete interests in the bipartite association, the presence of single strains of Pseudonocardia within colonies may not be in the best interest of the ants, because increasing the diversity of bacteria, and thereby antibiotic diversity, would help the ant-fungus mutualism deal with the specialized parasites.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Leigh EG., Jr . Levels of selection, potential conflicts, and their resolution: The role of the “common good”. In: Keller L, editor. Levels of selection in evolution. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press; 1999. pp. pp. 15–30.
-
- Hardin G. The tragedy of the commons. Science. 1968;162:1243–1248. - PubMed
-
- Ratnieks FLW, Foster KR, Wenseleers T. Conflict resolution in insect societies. Annu Rev Entomol. 2006;51:581–608. - PubMed
-
- Herre EA, Knowlton N, Mueller UG, Rehner SA. The evolution of mutualisms: exploring the paths between conflicts and cooperation. Trends Ecol Evol. 1999;14:49–53. - PubMed
-
- Frank SA. Host-symbiont conflict over the mixing of symbiotic lineages. Proc Roy Soc Lond B. 1996;263:339–344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

