Natural and synthetic polymers as inhibitors of drug efflux pumps
- PMID: 17896100
- PMCID: PMC2265773
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-007-9347-8
Natural and synthetic polymers as inhibitors of drug efflux pumps
Abstract
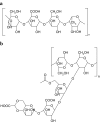
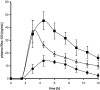
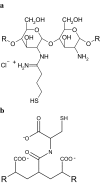
Inhibition of efflux pumps is an emerging approach in cancer therapy and drug delivery. Since it has been discovered that polymeric pharmaceutical excipients such as Tweens or Pluronics can inhibit efflux pumps, various other polymers have been investigated regarding their potential efflux pump inhibitory activity. Among them are polysaccharides, polyethylene glycols and derivatives, amphiphilic block copolymers, dendrimers and thiolated polymers. In the current review article, natural and synthetic polymers that are capable of inhibiting efflux pumps as well as their application in cancer therapy and drug delivery are discussed.
Figures





Similar articles
-
In vivo evaluation of anionic thiolated polymers as oral delivery systems for efflux pump inhibition.Int J Pharm. 2015 Aug 1;491(1-2):318-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2015.06.023. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Int J Pharm. 2015. PMID: 26095915
-
Reversal of multidrug resistance by the inhibition of ATP-binding cassette pumps employing "Generally Recognized As Safe" (GRAS) nanopharmaceuticals: A review.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013 Nov;65(13-14):1828-51. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2013.09.002. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013. PMID: 24055628 Review.
-
Poloxamines display a multiple inhibitory activity of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters in cancer cell lines.Mol Pharm. 2011 Aug 1;8(4):1152-64. doi: 10.1021/mp2000132. Epub 2011 Jun 7. Mol Pharm. 2011. PMID: 21591727
-
Inhibitors of bacterial efflux pumps that also inhibit efflux pumps of cancer cells.Anticancer Res. 2012 Jul;32(7):2947-57. Anticancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22753759 Review.
-
Marine natural products as breast cancer resistance protein inhibitors.Mar Drugs. 2015 Apr 3;13(4):2010-29. doi: 10.3390/md13042010. Mar Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25854646 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-Modulation of Doxorubicin Resistance in Breast Cancer Cells by Poly(l-histidine)-Based Multifunctional Micelles.Pharmaceutics. 2019 Aug 2;11(8):385. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11080385. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 31382390 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of P-Glycoprotein Inhibitor and Formulation of Combinational Nanoformulation Containing Selected Agent Curcumin and DOX for Reversal of Resistance in K562 Cells.Pharm Res. 2017 Aug;34(8):1741-1750. doi: 10.1007/s11095-017-2182-7. Epub 2017 May 23. Pharm Res. 2017. PMID: 28536971
-
Role of natural P-gp inhibitor in the effective delivery for chemotherapeutic agents.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Jan;149(1):367-391. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04387-2. Epub 2022 Oct 21. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36269390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Oral Drug Delivery.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Feb 19;12:618411. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.618411. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33679401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-ionic Surfactants as a P-Glycoprotein(P-gp) Efflux Inhibitor for Optimal Drug Delivery-A Concise Outlook.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2022 Jan 18;23(1):55. doi: 10.1208/s12249-022-02211-1. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2022. PMID: 35043278 Review.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/0005-2736(76)90160-7', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2736(76)90160-7'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '990323', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/990323/'}]}
- R. L. Juliano and V. Ling. A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta455:152–162 (1976). - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1073/pnas.84.21.7735', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.84.21.7735'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC299375', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC299375/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '2444983', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2444983/'}]}
- F. Thiebaut, T. Tsuruo, H. Hamada, M. M. Gottesman, I. Pastan, and M. C. Willingham. Cellular localization of the multidrug-resistance gene product P-glycoprotein in normal human tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.84:7735–7738 (1987). - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '1974900', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1974900/'}]}
- C. Cordon-Cardo, J. P. O’Brien, J. Boccia, D. Casals, J. R. Bertino, and M. R. Melamed. Expression of the multidrug resistance gene product (P-glycoprotein) in human normal and tumor tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem.38:1277–1287 (1990). - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC3181821', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3181821/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17117613', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17117613/'}]}
- F. Girardin. Membrane transporter proteins: a challenge for CNS drug development. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci.8:311–321 (2006). - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/j.addr.2004.02.006', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2004.02.006'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15191791', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15191791/'}]}
- S. Majumdar, S. Duvvuri, and A. K. Mitra. Membrane transporter/receptor-targeted prodrug design: strategies for human and veterinary drug development. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev.56:1437–1452 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

