Second cancers after fractionated radiotherapy: stochastic population dynamics effects
- PMID: 17897680
- PMCID: PMC2169295
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2007.07.034
Second cancers after fractionated radiotherapy: stochastic population dynamics effects
Abstract
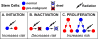
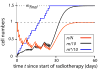
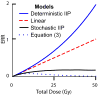
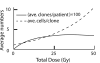
When ionizing radiation is used in cancer therapy it can induce second cancers in nearby organs. Mainly due to longer patient survival times, these second cancers have become of increasing concern. Estimating the risk of solid second cancers involves modeling: because of long latency times, available data is usually for older, obsolescent treatment regimens. Moreover, modeling second cancers gives unique insights into human carcinogenesis, since the therapy involves administering well-characterized doses of a well-studied carcinogen, followed by long-term monitoring. In addition to putative radiation initiation that produces pre-malignant cells, inactivation (i.e. cell killing), and subsequent cell repopulation by proliferation, can be important at the doses relevant to second cancer situations. A recent initiation/inactivation/proliferation (IIP) model characterized quantitatively the observed occurrence of second breast and lung cancers, using a deterministic cell population dynamics approach. To analyze if radiation-initiated pre-malignant clones become extinct before full repopulation can occur, we here give a stochastic version of this IIP model. Combining Monte-Carlo simulations with standard solutions for time-inhomogeneous birth-death equations, we show that repeated cycles of inactivation and repopulation, as occur during fractionated radiation therapy, can lead to distributions of pre-malignant cells per patient with variance>>mean, even when pre-malignant clones are Poisson-distributed. Thus fewer patients would be affected, but with a higher probability, than a deterministic model, tracking average pre-malignant cell numbers, would predict. Our results are applied to data on breast cancers after radiotherapy for Hodgkin disease. The stochastic IIP analysis, unlike the deterministic one, indicates: (a) initiated, pre-malignant cells can have a growth advantage during repopulation, not just during the longer tumor latency period that follows; (b) weekend treatment gaps during radiotherapy, apart from decreasing the probability of eradicating the primary cancer, substantially increase the risk of later second cancers.
Figures
References
-
- Bennett J, et al. Flexible dose-response models for Japanese atomic bomb survivor data: Bayesian estimation and prediction of cancer risk. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2004;43:233–45. - PubMed
-
- Boucher K, et al. A model of multiple tumorigenesis allowing for cell death: quantitative insight into biological effects of urethane. Math Biosci. 1998;150:63–82. - PubMed
-
- Crawford-Brown DJ, Hofmann W. A generalized state-vector model for radiation-induced cellular transformation. Int J Radiat Biol. 1990;57:407–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

