Modulation of host metabolism as a target of new antivirals
- PMID: 17897752
- PMCID: PMC7103349
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2007.03.021
Modulation of host metabolism as a target of new antivirals
Abstract
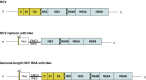
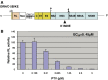
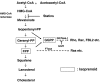
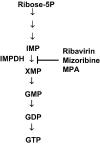
The therapy for chronic hepatitis C (CH-C) started with interferon (IFN) monotherapy in the early 1990s and this therapy was considered effective in about 10% of cases. The present standard therapy of pegylated IFN with ribavirin achieves a sustained virologic response in about 50% of patients. However, about half of the CH-C patients are still at risk of fatal liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. The other significant event in hepatitis C virus (HCV) research has been the development of a cell culture system. The subgenomic replicon system enables robust HCV RNA replication in hepatoma cells. And recently, the complete life cycle of HCV has been achieved using a genotype 2a strain, JFH1. These hallmarks have provided much information about the mechanisms of HCV replication, including information on the host molecules required for the replication. Anti-HCV reagents targeting HCV proteins have been developed, and some of them are now in clinical trials. However, the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase frequently causes mutations in the HCV genome, which lead to the emergence of drug-resistant HCV mutants. Some of the cellular proteins essential for HCV RNA replication have already been discovered using the HCV cell culture system. These host molecules are also candidate targets for antivirals. Here, we describe the recent progress regarding the anti-HCV reagents targeting host metabolism.
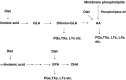
Figures

References
-
- Choo Q.L., Kuo G., Weiner A.J., Overby L.R., Bradley D.W., Houghton M. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science. 1989;244:359–362. - PubMed
-
- Report of a WHO Consultation organized in collaboration with the Viral Hepatitis Prevention Board, Antwerp, Belgium. vol. 6. 1999. Global surveillance and control of hepatitis C; pp. 35–47. (J Viral Hepat). - PubMed
-
- Hayashi N., Takehara T. Antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis C: past, present, and future. J. Gastroenterol. 2006;41:17–27. - PubMed
-
- Lohmann V., Korner F., Koch J., Herian U., Theilmann L., Bartenschlager R. Replication of subgenomic hepatitis C virus RNAs in a hepatoma cell line. Science. 1999;285:110–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

