Generation of a transgenic zebrafish model of Tauopathy using a novel promoter element derived from the zebrafish eno2 gene
- PMID: 17897967
- PMCID: PMC2095798
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm608
Generation of a transgenic zebrafish model of Tauopathy using a novel promoter element derived from the zebrafish eno2 gene
Abstract
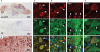
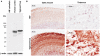
The aim of this study was to isolate cis-acting regulatory elements for the generation of transgenic zebrafish models of neurodegeneration. Zebrafish enolase-2 (eno2) showed neuronal expression increasing from 24 to 72 h post-fertilization (hpf) and persisting through adulthood. A 12 kb eno2 genomic fragment, extending from 8 kb upstream of exon 1 to exon 2, encompassing intron 1, was sufficient to drive neuronal reporter gene expression in vivo over a similar time course. Five independent lines of stable Tg(eno2 : GFP) zebrafish expressed GFP widely in neurons, including populations with relevance to neurodegeneration, such as cholinergic neurons, dopaminergic neurons and cerebellar Purkinje cells. We replaced the exon 2-GFP fusion gene with a cDNA encoding the 4-repeat isoform of the human microtubule-associated protein Tau. The first intron of eno2 was spliced with high fidelity and efficiency from the chimeric eno2-Tau transcript. Tau was expressed at approximately 8-fold higher levels in Tg(eno2 : Tau) zebrafish brain than normal human brain, and localized to axons, neuropil and ectopic neuronal somatic accumulations resembling neurofibrillary tangles. The 12 kb eno2 promoter drives high-level transgene expression in differentiated neurons throughout the CNS of stable transgenic zebrafish. This regulatory element will be useful for the construction of transgenic zebrafish models of neurodegeneration.
Figures

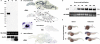




References
-
- Kimmel CB. Genetics and early development of zebrafish. Trends Genet. 1989;5:283–288. - PubMed
-
- Peters KG, Rao PS, Bell BS, Kindman LA. Green fluorescent fusion proteins: powerful tools for monitoring protein expression in live zebrafish embryos. Dev. Biol. 1995;171:252–257. - PubMed
-
- Thermes V, Grabher C, Ristoratore F, Bourrat F, Choulika A, Wittbrodt J, Joly JS. I-SceI meganuclease mediates highly efficient transgenesis in fish. Mech. Dev. 2002;118:91–98. - PubMed
-
- Guo S, Wilson SW, Cooke S, Chitnis AB, Driever W, Rosenthal A. Mutations in the zebrafish unmask shared regulatory pathways controlling the development of catecholaminergic neurons. Dev. Biol. 1999;208:473–487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

