A recombinant herpes simplex virus type 1 expressing two additional copies of gK is more pathogenic than wild-type virus in two different strains of mice
- PMID: 17898051
- PMCID: PMC2169076
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01442-07
A recombinant herpes simplex virus type 1 expressing two additional copies of gK is more pathogenic than wild-type virus in two different strains of mice
Abstract
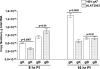
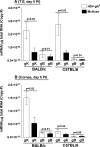
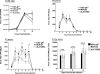
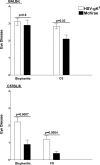
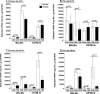
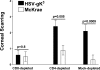
The effect of glycoprotein K (gK) overexpression on herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) infection in two different strains of mice was evaluated using a recombinant HSV-1 virus that expresses two additional copies of the gK gene in place of the latency-associated transcript (LAT). This mutant virus (HSV-gK3) expressed higher levels of gK than either the wild-type McKrae virus or the parental dLAT2903 virus both in vitro (in cultured cells) and in vivo (in infected mouse corneas and trigeminal ganglia [TG] of BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice). gK transcripts were detected in the TG of both HSV-gK3-infected mouse strains on day 30 postinfection (p.i.), while gB transcripts were detected only in the TG of the HSV-gK3-infected C57BL/6 mice, a finding that suggests that increased gK levels promote chronic infection. C57BL/6 mice infected with HSV-gK3 also contained free virus in their TG on day 30 p.i. Both HSV-gK3-infected mouse strains had significantly higher corneal scarring (CS) than did McKrae-infected mice. T-cell depletion studies in C57BL/6 mice suggested that this CS enhancement in the HSV-gK3-infected mice was mediated by a CD8+ T-cell response. Taken together, these results strongly suggest that increased gK levels promote eye disease and chronic infection in infected mice.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Overexpression of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein K (gK) alters expression of HSV receptors in ocularly-infected mice.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Apr 15;55(4):2442-51. doi: 10.1167/iovs.14-14013. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 24667863 Free PMC article.
-
The herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) glycoprotein K(gK) is essential for viral corneal spread and neuroinvasiveness.Curr Eye Res. 2008 May;33(5):455-67. doi: 10.1080/02713680802130362. Curr Eye Res. 2008. PMID: 18568883
-
An M2 Rather than a TH2 Response Contributes to Better Protection against Latency Reactivation following Ocular Infection of Naive Mice with a Recombinant Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Expressing Murine Interleukin-4.J Virol. 2018 Apr 27;92(10):e00051-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00051-18. Print 2018 May 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29491152 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations within the pathogenic region of herpes simplex virus 1 gK signal sequences alter cell surface expression and neurovirulence.J Virol. 2015 Mar;89(5):2530-42. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03506-14. Epub 2014 Dec 10. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25505072 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1) Glycoprotein K (gK) Pathogenic CD8+ T Cells in Exacerbation of Eye Disease.Front Immunol. 2018 Dec 7;9:2895. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02895. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30581441 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Absence of CD80 reduces HSV-1 replication in the eye and delays reactivation but not latency levels.J Virol. 2024 Mar 19;98(3):e0201023. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02010-23. Epub 2024 Feb 20. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38376148 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of signal peptide peptidase in peripheral sensory neurons affects latency-reactivation in HSV-1 ocularly infected mice.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Jan 31;18(1):e1010281. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010281. eCollection 2022 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35100323 Free PMC article.
-
Small Noncoding RNA (sncRNA1) within the Latency-Associated Transcript Modulates Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Virulence and the Host Immune Response during Acute but Not Latent Infection.J Virol. 2022 Apr 13;96(7):e0005422. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00054-22. Epub 2022 Mar 7. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35254102 Free PMC article.
-
The Latency-Associated Transcript Inhibits Apoptosis via Downregulation of Components of the Type I Interferon Pathway during Latent Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Ocular Infection.J Virol. 2019 May 1;93(10):e00103-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00103-19. Print 2019 May 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30814286 Free PMC article.
-
The Absence of DHHC3 Affects Primary and Latent Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection.J Virol. 2018 Jan 30;92(4):e01599-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01599-17. Print 2018 Feb 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29187538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banerjee, K., S. Deshpande, M. Zheng, U. Kumaraguru, S. P. Schoenberger, and B. T. Rouse. 2002. Herpetic stromal keratitis in the absence of viral antigen recognition. Cell Immunol. 219:108-118. - PubMed
-
- Berra, A., A. Rodriguez, A. Heiligenhaus, B. Pazos, N. Van Rooijen, and C. S. Foster. 1994. The role of macrophages in the pathogenesis of HSV-1 induced chorioretinitis in BALB/c mice. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 35:2990-2998. - PubMed
-
- Bond, V. C., and S. Person. 1984. Fine structure physical map locations of alterations that affect cell fusion in herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology 132:368-376. - PubMed
-
- Brandt, C. R. 2005. The role of viral and host genes in corneal infection with herpes simplex virus type 1. Exp. Eye Res. 80:607-621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

