Phosphorylated retinoid X receptor alpha loses its heterodimeric activity with retinoic acid receptor beta
- PMID: 17900311
- PMCID: PMC11159768
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00621.x
Phosphorylated retinoid X receptor alpha loses its heterodimeric activity with retinoic acid receptor beta
Abstract
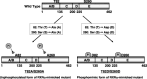
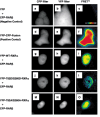
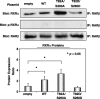
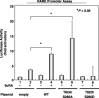
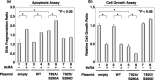
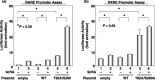
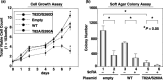
A malfunction in retinoid X receptor (RXR) alpha due to phosphorylation is associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. However, the precise mechanisms by which phosphorylated RXRalpha loses its physiological function remain unclear. In the present study we examined whether phosphorylation of RXRalpha affects its dimeric activity. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer studies and immunoprecipitation assays showed that the physical interaction between RXRalpha and retinoic acid receptor beta was impaired when 293T cells were transfected with phosphomimic mutant RXRalpha (T82D/S260D), whereas this interaction was activated at a level similar to wild-type RXRalpha-transfected cells when the cells were transfected with an unphosphorylated mutant RXRalpha (T82A/S260A). Treating the T82A/S260A-transfected cells with retinoid resulted in a significant increase in the transcriptional activities of the retinoic acid receptor responsive element and RXR responsive element promoters, whereas these transcriptional activities did not increase in the T82D/S260D-transfected cells. Transfection with T82A/S260A enhanced both the inhibition of cell growth and the induction of apoptosis caused by retinoid, although the T82D/S260D-transfected cells lost their responsiveness to retinoid. Moreover, transfection with T82A/S260A caused an inhibition of cell growth and a reduction of colony-forming ability in soft agar in HuH7 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. These findings suggest that phosphorylation of RXRalpha abolishes its ability to form homodimers and heterodimers with RXR and retinoic acid receptor beta, thus resulting in the loss of cell growth control and the acceleration of cancer development. In conclusion, the inhibition of RXRalpha phosphorylation and the restoration of its original function as a master regulator of nuclear receptors might therefore be an effective strategy for controlling cancer cell growth.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Strategy and mechanism for the prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma: phosphorylated retinoid X receptor alpha is a critical target for hepatocellular carcinoma chemoprevention.Cancer Sci. 2009 Mar;100(3):369-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.01045.x. Epub 2008 Dec 4. Cancer Sci. 2009. PMID: 19068086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The phosphorylated retinoid X receptor-α promotes diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in mice through the activation of β-catenin signaling pathway.Carcinogenesis. 2022 Apr 25;43(3):254-263. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgab099. Carcinogenesis. 2022. PMID: 34668523 Free PMC article.
-
High glucose-induced repression of RAR/RXR in cardiomyocytes is mediated through oxidative stress/JNK signaling.J Cell Physiol. 2012 Jun;227(6):2632-44. doi: 10.1002/jcp.23005. J Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 21882190 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the retinoid x receptor at the omega loop, modulates the expression of retinoic-acid-target genes with a promoter context specificity.Cell Signal. 2005 Oct;17(10):1229-39. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2004.12.006. Epub 2005 Jan 20. Cell Signal. 2005. PMID: 16038797
-
Increased retinoic acid responsiveness in lung carcinoma cells that are nonresponsive despite the presence of endogenous retinoic acid receptor (RAR) beta by expression of exogenous retinoid receptors retinoid X receptor alpha, RAR alpha, and RAR gamma.Cancer Res. 2001 Jan 15;61(2):556-64. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11212249
Cited by
-
Strategy and mechanism for the prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma: phosphorylated retinoid X receptor alpha is a critical target for hepatocellular carcinoma chemoprevention.Cancer Sci. 2009 Mar;100(3):369-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.01045.x. Epub 2008 Dec 4. Cancer Sci. 2009. PMID: 19068086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation of RXRα mediates the effect of JNK to suppress hepatic FGF21 expression and promote metabolic syndrome.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Nov;119(44):e2210434119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2210434119. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36282921 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of the structure-based non-genomic effects of the nuclear receptor RXRα.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2018 Aug 7;23:36. doi: 10.1186/s11658-018-0103-3. eCollection 2018. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30093910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The phosphorylated retinoid X receptor-α promotes diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in mice through the activation of β-catenin signaling pathway.Carcinogenesis. 2022 Apr 25;43(3):254-263. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgab099. Carcinogenesis. 2022. PMID: 34668523 Free PMC article.
-
Acyclic retinoid in chemoprevention of hepatocellular carcinoma: Targeting phosphorylated retinoid X receptor-α for prevention of liver carcinogenesis.J Carcinog. 2012;11:11. doi: 10.4103/1477-3163.100398. Epub 2012 Aug 30. J Carcinog. 2012. PMID: 23230390 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hansen LA, Sigman CC, Andreola F, Ross SA, Kelloff GJ, De Luca LM. Retinoids in chemoprevention and differentiation therapy. Carcinogenesis 2000; 21: 1271–9. - PubMed
-
- Dawson MI. The importance of vitamin A in nutrition. Curr Pharm Des 2000; 6: 311–25. - PubMed
-
- Dong D, Noy N. Heterodimer formation by retinoid X receptor: regulation by ligands and by the receptor's self association properties. Biochemistry 1998; 37: 10 691–700. - PubMed
-
- Matsushima‐Nishiwaki R, Shidoji Y, Nishiwaki S, Yamada T, Moriwaki H, Muto Y. Aberrant metabolism of retinoid X receptor proteins in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell Endocrinol 1996; 121: 179–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

