The temporal responses of protein synthesis, gene expression and cell signalling in human quadriceps muscle and patellar tendon to disuse
- PMID: 17901116
- PMCID: PMC2375459
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.142828
The temporal responses of protein synthesis, gene expression and cell signalling in human quadriceps muscle and patellar tendon to disuse
Abstract
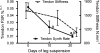
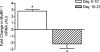
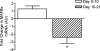
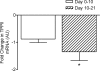
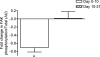
We hypothesized that rates of myofibrillar and patellar tendon collagen synthesis would fall over time during disuse, the changes being accompanied in muscle by decreases in focal adhesion kinase (FAK) phosphorylation and in gene expression for proteolytic enzymes. We studied nine men (22 +/- 4 years, BMI 24 +/- 3 kg m(-2) (means +/- s.d.) who underwent unilateral lower leg suspension for 23 days; five were studied between 0 and 10 days and four between 10 and 21 days. Muscle and tendon biopsies were taken in the postabsorptive state at days 0, 10 and 21 for measurement of protein synthesis, gene expression and protein phosphorylation. Muscle cross-sectional area decreased by 5.2% at 14 days and 10.0% (both P < 0.001), at 23 days, i.e. 0.5% day(-1), whereas tendon dimensions were constant. Rates of myofibrillar protein synthesis fell (P < 0.01) from 0.047% h(-1) at day 0 to 0.022% h(-1) at 10 days without further changes. Tendon collagen synthetic rates also fell (P < 0.01), from 0.052 to 0.023% h(-1) at 10 days and then to 0.010% h(-1) at 21 days. FAK phosphorylation decreased 30% (P < 0.01) at 10 days. No changes occurred in the amounts/phosphorylation of PKB-P70s6k-mTOR pathway components. Expression of mRNA for MuRF-1 increased approximately 3-fold at 10 days without changes in MAFbx or tripeptidyl peptidase II mRNA, but all decreased between 10 and 21 days. Thus, both myofibrillar and tendon protein synthetic rates show progressive decreases during 21 days of disuse; in muscle, this is accompanied by decreased phosphorylation of FAK, with no marked increases in genes for proteolytic enzymes.
Figures

References
-
- Babraj J, Cuthbertson DJ, Rickhuss P, Meier-Augenstein W, Smith K, Bohe J, Wolfe RR, Gibson JN, Adams C, Rennie MJ. Sequential extracts of human bone show differing collagen synthetic rates. Biochem Soc Trans. 2002;30:61–65. - PubMed
-
- Babraj JA, Cuthbertson DJ, Smith K, Langberg H, Miller B, Krogsgaard MR, Kjaer M, Rennie MJ. Collagen synthesis in human musculoskeletal tissues and skin. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2005a;289:E864–E869. - PubMed
-
- Babraj JA, Smith K, Cuthbertson DJ, Rickhuss P, Dorling JS, Rennie MJ. Human bone collagen synthesis is a rapid, nutritionally modulated process. J Bone Miner Res. 2005b;20:930–937. - PubMed
-
- Balagopal P, Ljungqvist O, Nair KS. Skeletal muscle myosin heavy-chain synthesis rate in healthy humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 1997;35:E45–E50. - PubMed
-
- Bodine SC, Stitt TN, Gonzalez M, Kline WO, Stover GL, Bauerlein R, Zlotchenko E, Scrimgeour A, Lawrence JC, Glass DJ, Yancopoulos GD. Akt/mTOR pathway is a crucial regulator of skeletal muscle hypertrophy and can prevent muscle atrophy in vivo. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3:1014–1019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

