Endurance exercise performance: the physiology of champions
- PMID: 17901124
- PMCID: PMC2375555
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.143834
Endurance exercise performance: the physiology of champions
Abstract
Efforts to understand human physiology through the study of champion athletes and record performances have been ongoing for about a century. For endurance sports three main factors--maximal oxygen consumption (.VO(2,max)), the so-called 'lactate threshold' and efficiency (i.e. the oxygen cost to generate a given running speed or cycling power output)--appear to play key roles in endurance performance. and lactate threshold interact to determine the 'performance .VO(2)' which is the oxygen consumption that can be sustained for a given period of time. Efficiency interacts with the performance .VO(2) to establish the speed or power that can be generated at this oxygen consumption. This review focuses on what is currently known about how these factors interact, their utility as predictors of elite performance, and areas where there is relatively less information to guide current thinking. In this context, definitive ideas about the physiological determinants of running and cycling efficiency is relatively lacking in comparison with .VO(2,max) and the lactate threshold, and there is surprisingly limited and clear information about the genetic factors that might pre-dispose for elite performance. It should also be cautioned that complex motivational and sociological factors also play important roles in who does or does not become a champion and these factors go far beyond simple physiological explanations. Therefore, the performance of elite athletes is likely to defy the types of easy explanations sought by scientific reductionism and remain an important puzzle for those interested in physiological integration well into the future.
Figures


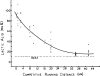
 (e.g. performance
(e.g. performance  ) that could be sustained in competition.
) that could be sustained in competition.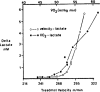
 . Trained subjects can usually exercise at 75–85% of
. Trained subjects can usually exercise at 75–85% of  before there is a marked increase in blood lactate concentration. This figure also illustrates the concept of performance
before there is a marked increase in blood lactate concentration. This figure also illustrates the concept of performance  and performance velocity.
and performance velocity.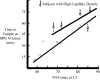
 values and uniformly high muscle oxidative enzymes. A subgroup of 4 athletes (subjects 1, 2, 7 and 8) with exceptionally high capillary density seemed to ‘overachieve’ in comparison with their lactate threshold values compared with other members of the group.
values and uniformly high muscle oxidative enzymes. A subgroup of 4 athletes (subjects 1, 2, 7 and 8) with exceptionally high capillary density seemed to ‘overachieve’ in comparison with their lactate threshold values compared with other members of the group.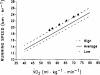
 and lactate threshold values. It is also of note that the physiological determinants of efficiency (especially for running) are poorly understood.
and lactate threshold values. It is also of note that the physiological determinants of efficiency (especially for running) are poorly understood.References
-
- Bangsbo J, Michalsik L, Petersen A. Accumulated O2 deficit during intense exercise and muscle characteristics of elite athletes. Int J Sports Med. 1993;14:207–213. - PubMed
-
- Bassett DR, Jr, Howley ET. Limiting factors for maximum oxygen uptake and determinants of endurance performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000;32:70–84. - PubMed
-
- Bosco C, Montanari G, Ribacchi R, Giovenali P, Latteri F, Iachelli G, Faina M, Colli R, Dal Monte A, La Rosa M. Relationship between the efficiency of muscular work during jumping and the energetics of running. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1987;56:138–143. - PubMed
-
- Chi M, Hintz CS, Coyle EF, Martin WH, 3rd, Ivy JL, Nemeth PM, Holloszy JO, Lowry OH. Effects of detraining on enzymes of energy metabolism in individual human muscle fibers. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 1983;244:C276–C287. - PubMed
-
- Christensen EH. Untersuchungen uber die Verbrennungsvorgange bei langdauernder, scwherer Muskelarbeit. Skand Arch Physiol. 1939;81:152–161.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

