Target-specific requirements for enhancers of decapping in miRNA-mediated gene silencing
- PMID: 17901217
- PMCID: PMC2000321
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.443107
Target-specific requirements for enhancers of decapping in miRNA-mediated gene silencing
Abstract
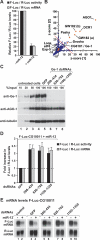
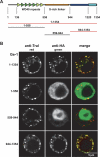
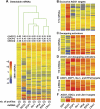
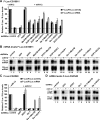
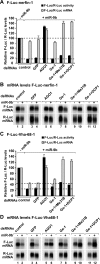
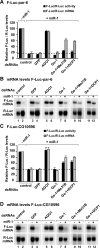
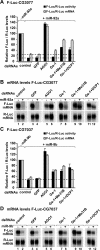
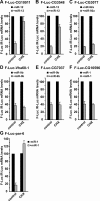
microRNAs (miRNAs) silence gene expression by suppressing protein production and/or by promoting mRNA decay. To elucidate how silencing is accomplished, we screened an RNA interference library for suppressors of miRNA-mediated regulation in Drosophila melanogaster cells. In addition to proteins known to be required for miRNA biogenesis and function (i.e., Drosha, Pasha, Dicer-1, AGO1, and GW182), the screen identified the decapping activator Ge-1 as being required for silencing by miRNAs. Depleting Ge-1 alone and/or in combination with other decapping activators (e.g., DCP1, EDC3, HPat, or Me31B) suppresses silencing of several miRNA targets, indicating that miRNAs elicit mRNA decapping. A comparison of gene expression profiles in cells depleted of AGO1 or of individual decapping activators shows that approximately 15% of AGO1-targets are also regulated by Ge-1, DCP1, and HPat, whereas 5% are dependent on EDC3 and LSm1-7. These percentages are underestimated because decapping activators are partially redundant. Furthermore, in the absence of active translation, some miRNA targets are stabilized, whereas others continue to be degraded in a miRNA-dependent manner. These findings suggest that miRNAs mediate post-transcriptional gene silencing by more than one mechanism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
mRNA degradation by miRNAs and GW182 requires both CCR4:NOT deadenylase and DCP1:DCP2 decapping complexes.Genes Dev. 2006 Jul 15;20(14):1885-98. doi: 10.1101/gad.1424106. Epub 2006 Jun 30. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16815998 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs silence gene expression by repressing protein expression and/or by promoting mRNA decay.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:523-30. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.013. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381335 Review.
-
A crucial role for GW182 and the DCP1:DCP2 decapping complex in miRNA-mediated gene silencing.RNA. 2005 Nov;11(11):1640-7. doi: 10.1261/rna.2191905. Epub 2005 Sep 21. RNA. 2005. PMID: 16177138 Free PMC article.
-
miRISC recruits decapping factors to miRNA targets to enhance their degradation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Oct;41(18):8692-705. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt619. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23863838 Free PMC article.
-
Argonaute-mediated translational repression (and activation).Fly (Austin). 2009 Jul-Sep;3(3):204-6. Epub 2009 Jul 14. Fly (Austin). 2009. PMID: 19556851 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of microRNAs in breast cancer.Cancer Biol Ther. 2013 Mar;14(3):201-12. doi: 10.4161/cbt.23296. Epub 2013 Jan 4. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23291983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Active site conformational dynamics are coupled to catalysis in the mRNA decapping enzyme Dcp2.Structure. 2013 Sep 3;21(9):1571-80. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2013.06.021. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Structure. 2013. PMID: 23911090 Free PMC article.
-
The GW/WG repeats of Drosophila GW182 function as effector motifs for miRNA-mediated repression.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Oct;38(19):6673-83. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq501. Epub 2010 Jun 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20530530 Free PMC article.
-
Immunopurification of Ago1 miRNPs selects for a distinct class of microRNA targets.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Sep 1;106(35):15085-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0908149106. Epub 2009 Aug 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19706460 Free PMC article.
-
Global phosphoproteomics identifies a major role for AKT and 14-3-3 in regulating EDC3.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010 Apr;9(4):682-94. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M900435-MCP200. Epub 2010 Jan 5. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010. PMID: 20051463 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bagga S., Bracht J., Hunter S., Massirer K., Holtz J., Eachus R., Pasquinelli A.E., Bracht J., Hunter S., Massirer K., Holtz J., Eachus R., Pasquinelli A.E., Hunter S., Massirer K., Holtz J., Eachus R., Pasquinelli A.E., Massirer K., Holtz J., Eachus R., Pasquinelli A.E., Holtz J., Eachus R., Pasquinelli A.E., Eachus R., Pasquinelli A.E., Pasquinelli A.E. Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell. 2005;122:553–563. - PubMed
-
- Bartel D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Behm-Ansmant I., Rehwinkel J., Doerks T., Stark A., Bork P., Izaurralde E., Rehwinkel J., Doerks T., Stark A., Bork P., Izaurralde E., Doerks T., Stark A., Bork P., Izaurralde E., Stark A., Bork P., Izaurralde E., Bork P., Izaurralde E., Izaurralde E. mRNA degradation by miRNAs and GW182 requires both CCR4:NOT deadenylase and DCP1:DCP2 decapping complexes. Genes & Dev. 2006a;20:1885–1898. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Behm-Ansmant I., Rehwinkel J., Izaurralde E., Rehwinkel J., Izaurralde E., Izaurralde E. MicroRNAs silence gene expression by repressing protein expression and/or by promoting mRNA decay. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2006b;71:523–530. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya S.N., Habermacher R., Martine U., Closs E.I., Filipowicz W., Habermacher R., Martine U., Closs E.I., Filipowicz W., Martine U., Closs E.I., Filipowicz W., Closs E.I., Filipowicz W., Filipowicz W. Relief of microRNA-mediated translational repression in human cells subjected to stress. Cell. 2006;125:1111–1124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
