Ozone exposure of macrophages induces an alveolar epithelial chemokine response through IL-1alpha
- PMID: 17901407
- PMCID: PMC2258451
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0250OC
Ozone exposure of macrophages induces an alveolar epithelial chemokine response through IL-1alpha
Abstract
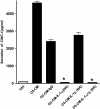
Ozone is known to produce an acute influx of neutrophils, and alveolar epithelial cells can secrete chemokines and modulate inflammatory processes. However, direct exposure of alveolar epithelial cells and macrophages to ozone (O(3)) produces little chemokine response. To determine if cell-cell interactions might be responsible, we investigated the effect of alveolar macrophage-conditioned media after ozone exposure (MO(3)CM) on alveolar epithelial cell chemokine production. Serum-free media were conditioned by exposing a rat alveolar macrophage cell line NR8383 to ozone for 1 hour. Ozone stimulated secretion of IL-1alpha, IL-1beta, and IL-18 from NR8383 cells, but there was no secretion of chemokines or TNF-alpha. Freshly isolated type II cells were cultured, so as to express the biological markers of type I cells, and these cells are referred to as type I-like cells. Type I-like cells were exposed to diluted MO(3)CM for 24 hours, and this conditioned medium stimulated secretion of cytokine-induced neutrophil chemattractant-1 (CXCL1) and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (CCL2). Secretion of these chemokines was inhibited by the IL-1 receptor antagonist. Although both recombinant IL-1alpha and IL-1beta stimulated alveolar epithelial cells to secrete chemokines, recombinant IL-1alpha was 100-fold more potent than IL-1beta. Furthermore, neutralizing anti-rat IL-1alpha antibodies inhibited the secretion of chemokines by alveolar epithelial cells, whereas neutralizing anti-rat IL-1beta antibodies had no effect. These observations indicate that secretion of IL-1alpha from macrophages stimulates alveolar epithelial cells to secrete chemokines that can elicit an inflammatory response.
Figures

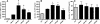
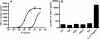
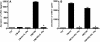
Similar articles
-
Alveolar epithelial cells secrete chemokines in response to IL-1beta and lipopolysaccharide but not to ozone.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006 Feb;34(2):158-66. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0205OC. Epub 2005 Oct 20. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16239643 Free PMC article.
-
Chemotaxis of alveolar macrophages in response to signals derived from alveolar epithelial cells.J Lab Clin Med. 1998 May;131(5):417-24. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2143(98)90142-1. J Lab Clin Med. 1998. PMID: 9605106
-
Differential regulation of cytokine release and leukocyte migration by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated primary human lung alveolar type II epithelial cells and macrophages.J Immunol. 2007 Jan 1;178(1):463-73. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.1.463. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17182585
-
Expression of CINC-2beta is related to the state of differentiation of alveolar epithelial cells.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2005 Nov;33(5):505-12. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0113OC. Epub 2005 Jul 29. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 16055671 Free PMC article.
-
Alveolar macrophages initiate the systemic microvascular inflammatory response to alveolar hypoxia.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2011 Sep 30;178(3):439-48. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2011.03.008. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21402178 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The IL-1 axis is associated with airway inflammation after O3 exposure in allergic asthmatic patients.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015 Oct;136(4):1099-101.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.03.035. Epub 2015 May 8. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25959670 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Antipollution skin protection - a new paradigm and its demonstration on two active compounds.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017 May 17;10:185-193. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S129437. eCollection 2017. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 28553131 Free PMC article.
-
The alarmin IL-1α is a master cytokine in acute lung inflammation induced by silica micro- and nanoparticles.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2014 Dec 13;11:69. doi: 10.1186/s12989-014-0069-x. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 25497724 Free PMC article.
-
Linezolid has unique immunomodulatory effects in post-influenza community acquired MRSA pneumonia.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 30;10(1):e0114574. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114574. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25635685 Free PMC article.
-
Lung macrophages: current understanding of their roles in Ozone-induced lung diseases.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2020 Apr;50(4):310-323. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2020.1762537. Epub 2020 May 27. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32458707 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Uysal N, Schapira RM. Effects of ozone on lung function and lung diseases. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2003;9:144–150. - PubMed
-
- Harkema JR, Wagner JG. Epithelial and inflammatory responses in the airways of laboratory rats coexposed to ozone and biogenic substances: enhancement of toxicant-induced airway injury. Exp Toxicol Pathol 2005;57:129–141. - PubMed
-
- Pino MV, Levin JR, Stovall MY, Hyde DM. Pulmonary inflammation and epithelial injury in response to acute ozone exposure in the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1992;112:64–72. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi N, Yu XY, Schofield BH, Kleeberger SR, Scott AL, Hasegawa S, Spannhake EW. Expression of ICAM-1 in airway epithelium after acute ozone exposure in the mouse. J Appl Physiol 1995;79:1753–1761. - PubMed
-
- Haddad EB, Salmon M, Koto H, Barnes PJ, Adcock I, Chung KF. Ozone induction of cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant (CINC) and nuclear factor-kappa b in rat lung: inhibition by corticosteroids. FEBS Lett 1996;379:265–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

