Review of twin and family studies on neuroanatomic phenotypes and typical neurodevelopment
- PMID: 17903108
- PMCID: PMC4038708
- DOI: 10.1375/twin.10.5.683
Review of twin and family studies on neuroanatomic phenotypes and typical neurodevelopment
Abstract
This article reviews the extant twin studies employing magnetic resonance imaging data (MRI), with an emphasis on studies of population-based samples. There have been approximately 75 twin reports using MRI, with somewhat under half focusing on typical brain structure. Of these, most are samples of adults. For large brain regions such as lobar volumes, the heritabilities of large brain volumes are consistently high, with genetic factors accounting for at least half of the phenotypic variance. The role of genetics in generating individual differences in the volumes of small brain regions is less clear, mostly due to a dearth of information, but rarely because of disagreement between studies. Multivariate analyses show strong genetic relationships between brain regions. Cortical regions involved in language, executive function, and emotional regulation appear to be more heritable than other areas. Studies of brain shape also show significant, albeit lower, genetic effects on population variance. Finally, there is evidence of significant genetically mediated relationships between intelligence and brain structure. At present, the majority of twin imaging studies are limited by sample sizes small by the standards of behavioral genetics; nevertheless the literature at present represents a pioneering effort in the pursuit of answers to many challenging neurobiological questions.
Figures
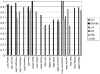
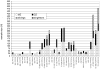
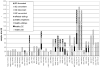
References
-
- Baaré WF, Hulshoff Pol HE, Boomsma DI, Posthuma D, De Geus EJ, Schnack HG, Van Haren NE, Van Oel CJ, Kahn RS. Quantitative genetic modeling of variation in human brain morphology. Cerebral Cortex. 2001a;11:816–824. - PubMed
-
- Baaré WF, van Oel CJ, Hulshoff Pol HE, Schnack HG, Durston S, Sitskoorn MM, Kahn RS. Volumes of brain structures in twins discordant for schizophrenia. Archives of General Psychiatry. 2001b;58:33–40. - PubMed
-
- Bartley AJ, Jones DW, Weinberger DR. Genetic variability of human brain size and cortical gyral patterns. Brain. 1997;120:257–269. - PubMed
-
- Bonan I, Argenti AM, Duyme M, Hasboun D, Dorion A, Marsault C, Souaoui A. Magnetic resonance imaging of cerebral central sulci: A study of monozygotic twins. Acta Geneticae Medicae et Gemellologiae. 1998;47:89–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AG022982/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH020030/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DA018673/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- AG-22982/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG-18386/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MH-65322/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG022381/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018386/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG-18384/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MH-20030/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DA-18673/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH065322/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018384/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG-22381/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA018673/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

