Multiple mechanisms modulate brassinosteroid signaling
- PMID: 17904409
- PMCID: PMC2093957
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbi.2007.08.015
Multiple mechanisms modulate brassinosteroid signaling
Abstract
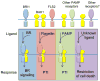
Brassinosteroids are essential hormones for plant growth and development. Genetic studies have identified key components of the BR signaling pathway, including the cell-surface receptor kinases that perceive BR, an intracellular kinase and a phosphatase, and nuclear transcription factors. Subsequent biochemical studies have revealed many details about signaling events from BR perception at the cell surface to gene expression in the nucleus. Recent studies have identified the 14-3-3 proteins as BR signaling components and elucidated multiple mechanisms by which phosphorylation modulates the BR transcription factors. In addition, BRI1 signaling from the endosomes and BR-independent functions of BAK1 have been observed. However, a major gap still exists in the current BR signaling pathway between the receptor complex and downstream signaling events.
Figures

References
-
- Li J, Chory J. A putative leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase involved in brassinosteroid signal transduction. Cell. 1997;90:929–938. - PubMed
-
- Kinoshita T, Cano-Delgado A, Seto H, Hiranuma S, Fujioka S, Yoshida S, Chory J. Binding of brassinosteroids to the extracellular domain of plant receptor kinase BRI1. Nature. 2005;433:167–171. - PubMed
-
- Wang JM, Asami T, Yoshida S, Murofushi N. Biological evaluation of 5-substituted pyrimidine derivatives as inhibitors of brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2001;65:817–822. - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Li X, Meisenhelder J, Hunter T, Yoshida S, Asami T, Chory J. Autoregulation and homodimerization are involved in the activation of the plant steroid receptor BRI1. Dev Cell. 2005;8:855–865. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

