Genetically delivered antibody protects against West Nile virus
- PMID: 17904654
- PMCID: PMC2267767
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2007.08.010
Genetically delivered antibody protects against West Nile virus
Abstract
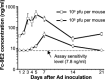
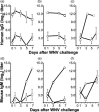
Gene-based delivery of recombinant antibody genes is a promising therapeutic strategy offering numerous advantages including sustained antibody levels, better safety profile and lower production cost. Here we describe generation of a recombinant antibody Fc-9E2 comprising a fusion protein between human Fc of IgG1 and a single-chain Fv derived from a hybridoma 9E2 secreting a mAb neutralizing West Nile virus (WNV). Fc-9E2 was shown to retain parental mAb's specificity and WNV-neutralizing capacity. Adenovirus-mediated in vivo delivery of the antibody gene resulted in sustained Fc-9E2 serum levels leading to abrogation of lethal WNV infection in an animal model.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Chimeric vaccine composed of viral peptide and mammalian heat-shock protein 60 peptide protects against West Nile virus challenge.Immunology. 2010 Aug;130(4):527-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2010.03251.x. Epub 2010 Mar 16. Immunology. 2010. PMID: 20331473 Free PMC article.
-
Immunization of flavivirus West Nile recombinant envelope domain III protein induced specific immune response and protection against West Nile virus infection.J Immunol. 2007 Mar 1;178(5):2699-705. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.5.2699. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17312111
-
Human Monoclonal Antibodies against NS1 Protein Protect against Lethal West Nile Virus Infection.mBio. 2021 Oct 26;12(5):e0244021. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02440-21. Epub 2021 Oct 12. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34634945 Free PMC article.
-
The structural immunology of antibody protection against West Nile virus.Immunol Rev. 2008 Oct;225:212-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00676.x. Immunol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18837784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The molecular basis of antibody protection against West Nile virus.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;317:125-53. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-72146-8_5. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 17990792 Review.
Cited by
-
A Scoping Review of Preclinical Research on Monoclonal Antibody Development for Prophylaxis and Treatment of West Nile Virus Infections.Viruses. 2025 Jun 12;17(6):845. doi: 10.3390/v17060845. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40573436 Free PMC article.
-
Human Monoclonal Fab Antibodies Against West Nile Virus and its Neutralizing Activity Analyzed in Vitro and in Vivo.J Antivir Antiretrovir. 2009 Nov 1;1(1):36-42. doi: 10.4172/jaa.1000005. J Antivir Antiretrovir. 2009. PMID: 20505850 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Efficacy of Vectored PGT121 Gene Delivery in HIV-1-Infected Humanized Mice.J Virol. 2018 Mar 14;92(7):e01925-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01925-17. Print 2018 Apr 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29321310 Free PMC article.
-
State of play and clinical prospects of antibody gene transfer.J Transl Med. 2017 Jun 7;15(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12967-017-1234-4. J Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28592330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vector-mediated gene transfer engenders long-lived neutralizing activity and protection against SIV infection in monkeys.Nat Med. 2009 Aug;15(8):901-6. doi: 10.1038/nm.1967. Epub 2009 May 17. Nat Med. 2009. PMID: 19448633 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alvarez R.D., Barnes M.N., Gomez-Navarro J., Wang M., Strong T.V., Arafat W., Arani R.B., Johnson M.R., Roberts B.L., Siegal G.P., Curiel D.T. A cancer gene therapy approach utilizing an anti-erbB-2 single-chain antibody-encoding adenovirus (AD21): a phase I trial. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2000;6:3081–3087. - PubMed
-
- Bakker J.M., Bleeker W.K., Parren P.W. Therapeutic antibody gene transfer: an active approach to passive immunity. Mol. Ther. 2004;10:411–416. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Nathan D., Lustig S., Tam G., Robinzon S., Segal S., Rager-Zisman B. Prophylactic and therapeutic efficacy of human intravenous immunoglobulin in treating West Nile virus infection in mice. J. Infect. Dis. 2003;188:5–12. - PubMed
-
- Breitling F., Dubel S., Seehaus T., Klewinghaus I., Little M. A surface expression vector for antibody screening. Gene. 1991;104:147–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

