Role of neuronal nitric oxide in the regulation of vasopressin expression and release in response to inhibition of catecholamine synthesis and dehydration
- PMID: 17904738
- PMCID: PMC2768346
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.08.066
Role of neuronal nitric oxide in the regulation of vasopressin expression and release in response to inhibition of catecholamine synthesis and dehydration
Abstract
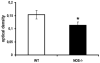
We used neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) gene knockout mice to study the effects of catecholamines and neuronal nitric oxide on vasopressin expression in the hypothalamic neurosecretory centers. nNOS gene deletion did not change the level of vasopressin mRNA in the supraoptic or paraventricular nuclei. In contrast, vasopressin immunoreactivity was lower in nNOS deficient mice than in wild-type animals. Dehydration increased vasopressin mRNA levels and decreased vasopressin immunoreactivity in both wild-type and nNOS knockout mice, but these responses were more marked in the nNOS knockout mice. Treatment with alpha-mpt, a pharmacologic inhibitor of catecholamine synthesis, resulted in increased vasopressin mRNA levels in wild-type mice and in reduced vasopressin immunoreactivity in both wild-type and nNOS knockout mice. From these results, we conclude: (1) neuronal nitric oxide suppresses vasopressin expression under basal conditions and during activation of the vasopressinergic system by dehydration; (2) catecholamines limit vasopressin expression; (3) nNOS is required for the effects of catecholamines on vasopressin expression.
Figures




References
-
- Scharrer E. Principles of neuroendocrine integration. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1966;43:1–35. - PubMed
-
- Sladek CD, Knigge KM. Osmotic control of vasopressin release by rat hypothalamo-neurohypophyseal explants in organ culture. Endocrinology. 1977;101:1834–8. - PubMed
-
- Shioda S, Nakai Y. Direct projections form catecholaminergic neurons in the caudal ventrolateral medulla to vasopressin-containing neurons in the supraoptic nucleus: a triple-labeling electron microscope study in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1996;221:45–8. - PubMed
-
- Takano T, Kubota Y, Wanaka A, Usuda S, Tanaka M, Malbon CC, Tohyama M. Beta-adrenergic receptors in the vasopressin-containing neurons in the paraventricular and supraoptic nucleus of the rat. Brain Res. 1989;499:174–8. - PubMed
-
- Ji Y, Mei J, Lu S. Opposing effects of intracerebroventricularly injected norepinephrine on oxytocin and vasopressin neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1998;244:13–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

