Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and prognosis of heart failure in the elderly
- PMID: 17905375
- PMCID: PMC5391148
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hfc.2007.07.004
Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and prognosis of heart failure in the elderly
Abstract
Heart failure (HF) represents the quintessential disorder of cardiovascular aging, reflecting the convergence of age-related changes in the cardiovascular system and other organ systems and the increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases at older age. The prevalence and incidence of HF increase progressively with advancing age, and HF imposes an enormous burden on society in mortality, morbidity, and associated health care costs. Despite major advances in treatment of HF over the last 25 years, the prognosis remains poor, with median survival rates of less than 5 years in older adults. As the population ages, it is anticipated that the number of older people with HF will increase dramatically over the next several decades.
Figures

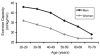

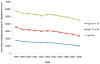


Republished from
-
Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and prognosis of heart failure in the elderly.Clin Geriatr Med. 2007 Feb;23(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2006.08.001. Clin Geriatr Med. 2007. PMID: 17126752 Review.
References
-
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. [on November 26, 2016];HCUP Statistical Brief 66: Medicare hospital stays: comparisons between the fee-for-service plan and alternative plans. 2006 Accessed at https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/statbriefs/sb66.jsp. - PubMed
-
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2013;128(16):e240–327. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

