Posttranslational processing of hepcidin in human hepatocytes is mediated by the prohormone convertase furin
- PMID: 17905609
- PMCID: PMC2211381
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2007.07.009
Posttranslational processing of hepcidin in human hepatocytes is mediated by the prohormone convertase furin
Abstract
Hepcidin is encoded as an 84 amino acid prepropeptide containing a typical N-terminal 24 amino acid endoplasmic reticulum targeting signal sequence, and a 35 amino acid proregion (pro) with a consensus furin cleavage site immediately followed by the C-terminal 25 amino acid bioactive iron-regulatory hormone (mature peptide). We performed pulse-chase studies of posttranslational processing of hepcidin in human hepatoma HepG2 cells and in primary human hepatocytes induced with bone morphogenic protein (BMP-9). In some experiments, the cells were treated with the furin protease inhibitor decanoyl-Arg-Val-Lys-Arg-chloromethylketone (CMK) or furin siRNA. In the absence of furin inhibitor, hepcidin was found to be processed in less than 1 h and secreted as a 3 kDa form reactive with anti-mature but not anti-pro antibody. In the presence of furin inhibitors or furin siRNA, a 6 kDa form reactive with both anti-pro and anti-mature antibody was rapidly secreted into the medium. Processing was not affected by inhibitors of the hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) pathway, or by treatment with 30 microM holo- or apo-transferrin. In conclusion, the hepatic prohormone convertase furin mediates the posttranslational processing of hepcidin. The proteolytic cleavage of prohepcidin to hepcidin is not regulated by iron-transferrin or the HIF pathway.
Figures



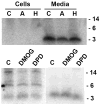
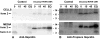
Comment in
-
Commentary to: "Post-translational processing of hepcidin in human hepatocytes is mediated by the prohormone convertase furin," by Erika Valore and Tomas Ganz.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2008 Jan-Feb;40(1):139-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2007.07.010. Epub 2007 Oct 1. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2008. PMID: 17905608 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Nemeth E, Tuttle MS, Powelson J, Vaughn MB, Donovan A, Ward DM, Ganz T, Kaplan J. Hepcidin regulates cellular iron efflux by binding to ferroportin and inducing its internalization. Science. 2004;306:2090–2093. - PubMed
-
- Pigeon C, Ilyin G, Courselaud B, Leroyer P, Turlin B, Brissot P, Loreal O. A new mouse liver-specific gene, encoding a protein homologous to human antimicrobial peptide hepcidin, is overexpressed during iron overload. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:7811–7819. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

