Prevention of salt induced hypertension and fibrosis by angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors in Dahl S rats
- PMID: 17906684
- PMCID: PMC2078219
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707472
Prevention of salt induced hypertension and fibrosis by angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors in Dahl S rats
Abstract
Background and purpose: In Dahl S rats, high salt increases activity of the tissue renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) in the CNS, heart and kidneys. Here, we assessed the effects of chronic angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibition on salt-induced hypertension and cardiovascular and renal hypertrophy and fibrosis, relative to the extent of ACE blockade.
Experimental approach: From 4.5 weeks of age, Dahl S rats received either the lipophilic ACE inhibitor trandolapril (1 or 5 mg kg(-1) day(-1)) or the hydrophilic ACE inhibitor lisinopril (10 or 50 mg kg(-1) day(-1)) and a high salt diet was started 0.5 week later. Treatments ended at 9 weeks of age.
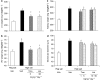
Key results: High salt diet markedly increased blood pressure (BP), decreased plasma angiotensin II and increased ACE binding densities in brain, heart, aorta and kidneys. Trandolapril and lisinopril prevented 50% of the increase in BP in light and dark period of the day. After the last doses, trandolapril decreased ACE densities by approximately 80% in brain nuclei and heart and lisinopril by approximately 60% in the brain and by approximately 70% in the heart. The two ACE inhibitors prevented right ventricular hypertrophy and attenuated left ventricular hypertrophy but did not affect renal hypertrophy caused by high salt. Both drugs prevented high salt-induced fibrosis in heart, kidney and aorta.
Conclusion and implication: As the ACE inhibitors could completely prevent tissue fibrosis and partially prevent tissue hypertrophy and hypertension, the tissue RAAS may play a critical role in salt-induced fibrosis, but a lesser role in the hypertrophy.
Figures
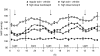




References
-
- Ashida T, Yoshimi H, Kawano Y, Matsuoka H, Omae T. Effect of cilazapril and salt on Ca2+ extrusion in arterial smooth muscle of Dahl rats. Am J Hypertens. 1997;10:107S–111S. - PubMed
-
- Baltatu O, Nishimura H, Hoffmann S, Stoltenburg G, Haulica ID, Lippoldt A, et al. High levels of human chymase expression in the pineal and pituitary glands. Brain Res. 1997;752:269–278. - PubMed
-
- Bayorh MA, Ganafa AA, Emmett N, Socci RR, Eatman D, Fridie II. Alterations in aldosterone and angiotensin II levels in salt-induced hypertension. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2005;27:355–367. - PubMed
-
- Bledsoe G, Shen B, Yao Y, Zhang JJ, Chao L, Chao J. Reversal of renal fibrosis, inflammation, and glomerular hypertrophy by kallikrein gene delivery. Hum Gene Ther. 2006;17:545–555. - PubMed
-
- Conen H, Brunner HR. Pharmacologic profile of trandolapril, a new angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. Am Heart J. 1993;125:1525–1531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

