The anticancer drug cisplatin induces an intrinsic apoptotic pathway inside the inner ear
- PMID: 17906689
- PMCID: PMC2095105
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707405
The anticancer drug cisplatin induces an intrinsic apoptotic pathway inside the inner ear
Abstract
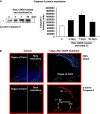
Background and purpose: Ototoxicity is a known adverse effect of cisplatin (CDDP). Since apoptosis is involved in the development of some pathological conditions associated with the administration of anticancer drugs, we examined, using immunohistochemical and electrophysiological techniques, the apoptotic changes in the cochlea of Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats after an injection of CDDP (5 mgkg(-1) body weight).
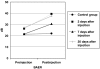
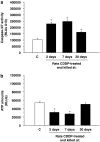
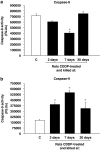
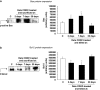
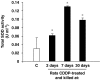
Experimental approach: Luciferase assays were used to determine the different caspase activities and ATP levels in protein extracts of whole cochleae. The expression of several apoptotic-related proteins was measured by means of Western blotting. These analyses were performed 2, 7 and 30 days after the CDDP injection. The auditory brain stem response was obtained before and at the different times after the injection of CDDP, before the animals were killed.
Key results: CDDP significantly increased the levels of caspase-3/7 activity and active caspase-3 protein expression and caspase-3 immunofluorescence staining, caspase-9 activity, and Bax protein expression but decreased Bcl-2 protein expression within the rat cochleae. Threshold shifts were significantly elevated 2 days after CDDP treatment.
Conclusions and implications: These findings support the hypothesis that cisplatin-related apoptosis evokes an intrinsic pathway of pro-apoptotic signalling within the rat cochleae. Thus, selective inhibition of the sequence of events involved in the intrinsic apoptotic pathway could provide a strategy to minimize cisplatin-induced ototoxicity.
Figures
References
-
- Alam SA, Ikeda K, Oshima T, Suzuki M, Kawase T, Kikuchi T, et al. Cisplatin-induced apoptotic cell death in Mongolian gerbil cochlea. Hear Res. 2000;141:28–38. - PubMed
-
- Anniko M, Sobin A. Cisplatin: evaluation of its ototoxic potential. Am J Otol. 1986;7:276–293. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM. Death receptors: signalling and modulation. Science. 1998;281:1305–1308. - PubMed
-
- Bohm S, Oriana S, Spatti G, Di Re F, Breasciani G, Pirovano C, et al. Dose intensification of platinum compounds with glutathione protection as induction chemotherapy for advanced ovarian carcinoma. Oncology. 1999;57:115–120. - PubMed
-
- Cardinaal RM, De Groot JC, Huizing EH, Smoorenburg GF, Veldman JE. Ultrastructural changes in the albino guinea pig cochlea at different survival times following cessation of 8-day cisplatin administration. Acta Otolaryngol. 2004;124:144–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

