Clinical effectiveness of a rehabilitation program integrating exercise, self-management, and active coping strategies for chronic knee pain: a cluster randomized trial
- PMID: 17907147
- PMCID: PMC2673355
- DOI: 10.1002/art.22995
Clinical effectiveness of a rehabilitation program integrating exercise, self-management, and active coping strategies for chronic knee pain: a cluster randomized trial
Abstract
Objective: Chronic knee pain is a major cause of disability and health care expenditure, but there are concerns about efficacy, cost, and side effects associated with usual primary care. Conservative rehabilitation may offer a safe, effective, affordable alternative. We compared the effectiveness of a rehabilitation program integrating exercise, self-management, and active coping strategies (Enabling Self-management and Coping with Arthritic Knee Pain through Exercise [ESCAPE-knee pain]) with usual primary care in improving functioning in persons with chronic knee pain.
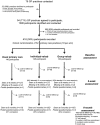
Methods: We conducted a single-blind, pragmatic, cluster randomized controlled trial. Participants age >/=50 years, reporting knee pain for >6 months, were recruited from 54 inner-city primary care practices. Primary care practices were randomized to continued usual primary care (i.e., whatever intervention a participant's primary care physician deemed appropriate), usual primary care plus the rehabilitation program delivered to individual participants, or usual primary care plus the rehabilitation program delivered to groups of 8 participants. The primary outcome was self-reported functioning (Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index physical functioning [WOMAC-func]) 6 months after completing rehabilitation.
Results: A total of 418 participants were recruited; 76 (18%) withdrew, only 5 (1%) due to adverse events. Rehabilitated participants had better functioning than participants continuing usual primary care (-3.33 difference in WOMAC-func score; 95% confidence interval [95% CI] -5.88, -0.78; P = 0.01). Improvements were similar whether participants received individual rehabilitation (-3.53; 95% CI -6.52, -0.55) or group rehabilitation (-3.16; 95% CI -6.55, -0.12).
Conclusion: ESCAPE-knee pain provides a safe, relatively brief intervention for chronic knee pain that is equally effective whether delivered to individuals or groups of participants.
Figures
References
-
- Dawson J, Linsell L, Zondervan K, Rose P, Randall T, Carr A, et al. Epidemiology of hip and knee pain and its impact on overall health status in older adults. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2004;43:497–504. - PubMed
-
- Alonso J, Ferrer M, Gandek B, Ware JE, Aaronson NK, Mosconi P, et al. Health-related quality of life associated with chronic conditions in eight countries: results from the International Quality of Life Assessment (IQOLA) Project. Qual Life Res. 2004;13:283–98. - PubMed
-
- Cooper JK, Kohlmann T. Factors associated with health status of older Americans. Age Ageing. 2001;30:495–501. - PubMed
-
- Gatchel RJ. Psychological disorders and chronic pacause and effect relationships. In: Gatchel RJ, Turk DC, editors. Psychological approaches to pain management: a practitioner's handbook. New York: Guildford Press; 1996. pp. 33–52.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical