Ribavirin and IFN-alpha combination therapy induces CD4+ T-cell proliferation and Th1 cytokine secretion in patients with chronic hepatitis B
- PMID: 17907286
- PMCID: PMC4171277
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i41.5440
Ribavirin and IFN-alpha combination therapy induces CD4+ T-cell proliferation and Th1 cytokine secretion in patients with chronic hepatitis B
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the anti-viral mechanism of combination therapy of interferon (IFN)-alpha and ribavirin in patients with chronic hepatitis B.
Methods: Twenty patients were assigned to receive either IFN-alpha plus ribavirin (group A, n = 14) or no treatment as a control (group B, n = 6). Patients were analyzed for T-cell proliferative responses specific for hepatitis B virus (HBV)-antigen and cytokine production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs).
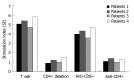
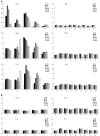
Results: Combination therapy induced HBV-antigen specific CD4+ T-cell proliferative responses in four patients (28.6%). Production of high levels of HBV-specific IFN-gamma, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interleukin (IL)-12 by PBMCs was found in five patients (35.7%), who showed significantly lower HBV DNA levels in serum at 12 mo after treatment ended (P = 0.038) and at 24 mo of follow-up (P = 0.004) than those without high levels of cytokine production.
Conclusion: HBV-antigen specific CD4+ T cells may directly control HBV replication and secretion of anti-viral T helper 1 (Th1) cytokines by PBMCs during combination therapy of chronic hepatitis B with ribavirin and IFN-alpha.
Figures
References
-
- Lai CL, Ratziu V, Yuen MF, Poynard T. Viral hepatitis B. Lancet. 2003;362:2089–2094. - PubMed
-
- Chisari FV, Ferrari C. Hepatitis B virus immunopathogenesis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:29–60. - PubMed
-
- Wong DK, Cheung AM, O'Rourke K, Naylor CD, Detsky AS, Heathcote J. Effect of alpha-interferon treatment in patients with hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. A meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 1993;119:312–323. - PubMed
-
- Sokal E. Drug treatment of pediatric chronic hepatitis B. Paediatr Drugs. 2002;4:361–369. - PubMed
-
- Lai CL, Chien RN, Leung NW, Chang TT, Guan R, Tai DI, Ng KY, Wu PC, Dent JC, Barber J, et al. A one-year trial of lamivudine for chronic hepatitis B. Asia Hepatitis Lamivudine Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:61–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

