Development of a novel mouse model to evaluate drug candidates against hepatitis B virus
- PMID: 17907379
- PMCID: PMC7656857
- DOI: 10.1177/095632020701800405
Development of a novel mouse model to evaluate drug candidates against hepatitis B virus
Abstract
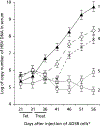
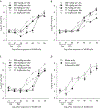
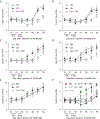
Woodchuck hepatitis virus (WHV)-infected woodchucks have been used for preclinical development of drugs against hepatitis B virus (HBV). However, there is no simple in vivo model to evaluate small amounts of compounds against HBV. To develop such a model, HepAD38 cells, in which HBV replication is regulated by tetracycline (tet), were grown as subcutaneous tumours in nude mice. Mice developing viraemia were then left untreated or given tet in the drinking water. In some of the mice given tet, it was removed and the mice were injected intraperitoneally with phosphate buffer saline (PBS), lamivudine (3TC), clevudine (CLV) or tenofovir dipivoxil fumarate (TDF). Virus DNA titres were measured by real-time PCR during and after drug treatment. In water-fed and PBS-injected mice, virus titres reached approximately 10(9) copies/ml serum within 35 days of HepAD38 injection, whereas in tet-treated mice, virus titres remained at 10(4)-10(5) copies/ml. HBV DNA levels were suppressed by 3TC, TDF and CLV, with the latter two drugs showing more sustained virus suppression compared with 3TC. Combination therapy with CLV plus TDF was much more effective than either drug alone in suppressing virus titre for at least 3 weeks after the end of treatment. There was no demonstrable toxicity to HepAD38 cells in drug-treated mice. Hence, a robust tet-controlled system for HBV replication in vivo was demonstrated, validated with monotherapies against HBV and shown to be useful in assessing combination therapy. This system will be useful for preclinical assessment of small amounts of single or multiple compounds against HBV in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson AL, Banks KE, Pontoglio M, Yaniv M & McLachlan A (2005) Alpha/beta interferon differentially modulates the clearance of cytoplasmic encapsidated replication intermediates and nuclear covalently closed circular hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA from the livers of hepatocyte nuclear factor 1alpha-null HBV transgenic mice. Journal of Virology 79:11045–11052. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bijsterbosch MK, Ying C, de Vrueh RL, de Clercq E, Biessen EA, Neyts J & van Berkel TJ (2001) Carrier-mediated delivery improves the efficacy of 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl)adenine against hepatitis B virus. Molecular Pharmacology 60:521–527. - PubMed
-
- Bouchard MJ, Wang LH & Schneider RJ (2001) Calcium signaling by HBx protein in hepatitis B virus DNA replication. Science 294:2376–2378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

