Viral oncogene-induced DNA damage response is activated in Kaposi sarcoma tumorigenesis
- PMID: 17907806
- PMCID: PMC1994968
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030140
Viral oncogene-induced DNA damage response is activated in Kaposi sarcoma tumorigenesis
Abstract
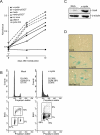
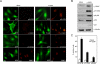
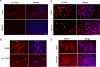
Kaposi sarcoma is a tumor consisting of Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus (KSHV)-infected tumor cells that express endothelial cell (EC) markers and viral genes like v-cyclin, vFLIP, and LANA. Despite a strong link between KSHV infection and certain neoplasms, de novo virus infection of human primary cells does not readily lead to cellular transformation. We have studied the consequences of expression of v-cyclin in primary and immortalized human dermal microvascular ECs. We show that v-cyclin, which is a homolog of cellular D-type cyclins, induces replicative stress in ECs, which leads to senescence and activation of the DNA damage response. We find that antiproliferative checkpoints are activated upon KSHV infection of ECs, and in early-stage but not late-stage lesions of clinical Kaposi sarcoma specimens. These are some of the first results suggesting that DNA damage checkpoint response also functions as an anticancer barrier in virally induced cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Bartkova J, Rezaei N, Liontos M, Karakaidos P, Kletsas D, et al. Oncogene-induced senescence is part of the tumorigenesis barrier imposed by DNA damage checkpoints. Nature. 2006;444:633–637. - PubMed
-
- Gorgoulis VG, Vassiliou LV, Karakaidos P, Zacharatos P, Kotsinas A, et al. Activation of the DNA damage checkpoint and genomic instability in human precancerous lesions. Nature. 2005;434:907–913. - PubMed
-
- Vafa O, Wade M, Kern S, Beeche M, Pandita TK, et al. c-Myc can induce DNA damage, increase reactive oxygen species, and mitigate p53 function: A mechanism for oncogene-induced genetic instability. Mol Cell. 2002;9:1031–1044. - PubMed
-
- Lindstrom MS, Wiman KG. Myc and E2F1 induce p53 through p14ARF-independent mechanisms in human fibroblasts. Oncogene. 2003;22:4993–5005. - PubMed
-
- Di Micco R, Fumagalli M, Cicalese A, Piccinin S, Gasparini P, et al. Oncogene-induced senescence is a DNA damage response triggered by DNA hyper-replication. Nature. 2006;444:638–642. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

