Genetics of aging in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 17907808
- PMCID: PMC1994694
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030129
Genetics of aging in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
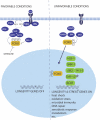
A dissection of longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans reveals that animal life span is influenced by genes, environment, and stochastic factors. From molecules to physiology, a remarkable degree of evolutionary conservation is seen.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. The author has declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Kenyon C, Chang J, Gensch E, Rudner A, Tabtiang R. A C. elegans mutant that lives twice as long as wild type. Nature. 1993;366:461–464. - PubMed
-
- Morris JZ, Tissenbaum HA, Ruvkun G. A phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase family member regulating longevity and diapause in C. elegans. Nature. 1996;382:536–539. - PubMed
-
- Kimura KD, Tissenbaum HA, Liu Y, Ruvkun G. daf-2, an insulin receptor-like gene that regulates longevity and diapause in C. elegans. Science. 1997;277:942–946. - PubMed
-
- Ogg S, Paradis S, Gottlieb S, Patterson GI, Lee L, et al. The Fork head transcription factor DAF-16 transduces insulin-like metabolic and longevity signals in C. elegans. Nature. 1997;389:994–999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical