Cellular learning theory: theoretical comment on Cole and McNally (2007)
- PMID: 17907848
- PMCID: PMC7247428
- DOI: 10.1037/0735-7044.121.5.1140
Cellular learning theory: theoretical comment on Cole and McNally (2007)
Abstract
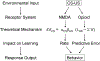
The idea that learning proceeds as a function of the discrepancy (or error) between expected and obtained outcomes is central to many theories of associative learning. However, remarkably little is known about the neurobiological mechanisms that underlie this learning of predictive errors in fear conditioning, a widely used preparation in studies of cellular and molecular mechanisms of memory. In this issue of Behavioral Neuroscience, S. Cole and G. P. McNally demonstrate an important dissociation between the establishment and regulation of predictive error at the cellular level. Their findings have added a level of complexity to currently established views of the function of NMDA and opioid receptors in learning and memory. This commentary discusses some of the implications of these findings for theoretical and neurobiological approaches to memory, as well as current thinking about the cellular circuitry involved in reward learning and drug abuse.
(PsycINFO Database Record (c) 2007 APA, all rights reserved).
Figures
Comment on
-
Temporal-difference prediction errors and Pavlovian fear conditioning: role of NMDA and opioid receptors.Behav Neurosci. 2007 Oct;121(5):1043-52. doi: 10.1037/0735-7044.121.5.1043. Behav Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17907835
References
-
- Abel T and Lattal KM (2001). Molecular mechanisms of memory acquisition, consolidation and retrieval. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11, 180–7. - PubMed
-
- Bechtholt AJ, & Cunningham CL (2005). Ethanol-induced conditioned place preference is expressed through a ventral tegmental area dependent mechanism. Behav Neurosci, 119(1), 213–223. - PubMed
-
- Bormann NM, & Cunningham CL (1997). The effects of naloxone on expression and acquisition of ethanol place conditioning in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 58(4), 975–982. - PubMed
-
- Brandon SE, Vogel EH and Wagner AR (2003). Stimulus representation in SOP: I. Theoretical rationalization and some implications. Behav Processes 62, 5–25. - PubMed
-
- Di Chiara G, & Imperato A (1988). Opposite effects of mu and kappa opiate agonists on dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens and in the dorsal caudate of freely moving rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 244(3), 1067–1080. - PubMed

