Down-regulation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase by over-activated calpain in Alzheimer disease brain
- PMID: 17908236
- PMCID: PMC2262109
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04942.x
Down-regulation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase by over-activated calpain in Alzheimer disease brain
Abstract
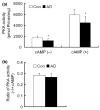
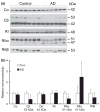
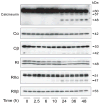
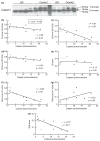
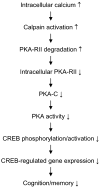
Impaired cognition and memory may be associated with down-regulation of cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB) in the brain in patients with Alzheimer disease, but the molecular mechanism leading to the down-regulation is not understood. In this study, we found a selective reduction in the levels of the regulatory subunits (RIIalpha and RIIbeta) and the catalytic subunit (Cbeta) as well as the enzymatic activity of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA), which is the major positive regulator of CREB. We also observed that PKA subunits were proteolyzed by calpain and the levels of PKA subunits correlated negatively with calpain activation in the human brain. These findings led us to propose that in the brain in patients with Alzheimer disease, over-activation of calpain because of calcium dysregulation causes increased degradation and thus decreased activity of PKA, which, in turn, contributes to down-regulation of CREB and impaired cognition and memory.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CREB regulates the expression of neuronal glucose transporter 3: a possible mechanism related to impaired brain glucose uptake in Alzheimer's disease.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Mar 1;41(5):3240-56. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1227. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23341039 Free PMC article.
-
The differential response of protein kinase A to cyclic AMP in discrete brain areas correlates with the abundance of regulatory subunit II.J Neurochem. 1996 Apr;66(4):1752-61. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1996.66041752.x. J Neurochem. 1996. PMID: 8627334
-
Human tau may modify glucocorticoids-mediated regulation of cAMP-dependent kinase and phosphorylated cAMP response element binding protein.Neurochem Res. 2012 May;37(5):935-47. doi: 10.1007/s11064-011-0686-9. Neurochem Res. 2012. PMID: 22294156
-
Alteration of second messengers during acute cerebral ischemia - adenylate cyclase, cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, and cyclic AMP response element binding protein.Prog Neurobiol. 2001 Oct;65(2):173-207. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(01)00002-8. Prog Neurobiol. 2001. PMID: 11403878 Review.
-
Swimming regulations for protein kinase A catalytic subunit.Biochem Soc Trans. 2019 Oct 31;47(5):1355-1366. doi: 10.1042/BST20190230. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019. PMID: 31671183 Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic effects of amyloid peptides and lead on human neuroblastoma cells.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2012 Sep;17(3):408-21. doi: 10.2478/s11658-012-0018-3. Epub 2012 May 18. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22610977 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Melatonin on Glutamate: BDNF Signaling in the Cerebral Cortex of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs)-Exposed Adult Male Rats.Neurochem Res. 2015 Sep;40(9):1858-69. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1677-z. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Neurochem Res. 2015. PMID: 26224288
-
The neuroprotective effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease: An in-depth review.Front Neurosci. 2022 Sep 1;16:970925. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.970925. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36117625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic stress and Alzheimer's disease-like pathogenesis in a rat model: prevention by nicotine.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2011 Dec;9(4):587-97. doi: 10.2174/157015911798376307. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2011. PMID: 22654719 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium, calpain, and calcineurin in low-frequency depression of transmitter release.J Neurosci. 2013 Jan 30;33(5):1975-90. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3092-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23365236 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aragon B, Poussard S, Dulong S, Touyarot K, Dargelos E, Brustis JJ, Levieux D, Ducastaing A, Cottin P. Protein kinase Calpha is a calpain target in cultured embryonic muscle cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2002;231:97–106. - PubMed
-
- Barco A, Pittenger C, Kandel ER. CREB, memory enhancement and the treatment of memory disorders: promises, pitfalls and prospects. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2003;7:101–114. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Staging of Alzheimer’s disease-related neurofibrillary changes. Neurobiol Aging. 1995;16:271–284. - PubMed
-
- Burton KA, Johnson BD, Hausken ZE, Westenbroek RE, Idzerda RL, Scheuer T, Scott JD, Catterall WA, McKnight GS. Type II regulatory subunits are not required for the anchoring-dependent modulation of Ca2+ channel activity by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:11067–11072. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cadd G, McKnight GS. Distinct patterns of cAMP-dependent protein kinase gene expression in mouse brain. Neuron. 1989;3:71–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

