X-ray structures of two proteins belonging to Pfam DUF178 revealed unexpected structural similarity to the DUF191 Pfam family
- PMID: 17908300
- PMCID: PMC2174479
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6807-7-62
X-ray structures of two proteins belonging to Pfam DUF178 revealed unexpected structural similarity to the DUF191 Pfam family
Abstract
Background: Pfam is a comprehensive collection of protein domains and families, with a range of well-established information including genome annotation. Pfam has two large series of functionally uncharacterized families, known as Domains of Unknown Function (DUFs) and Uncharacterized Protein Families (UPFs).
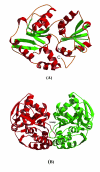
Results: Crystal structures of two proteins from Deinococcus radiodurans and Streptomyces coelicolor belonging to Pfam protein family DUF178 (ID: PF02621) have been determined using Selenium-Single-wavelength Anomalous Dispersion (Se-SAD). Based on the structure, we have identified the putative function for this family of protein.
Conclusion: Unexpectedly, we found that DUF178 Pfam is remarkably similar to Pfam family DUF191 suggesting that the sequence-based classification alone may not be sufficient to classify proteins into Pfam families.
Figures

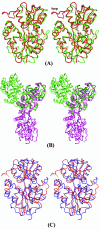
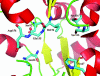
Similar articles
-
Structural and phylogenetic analysis of a conserved actinobacteria-specific protein (ASP1; SCO1997) from Streptomyces coelicolor.BMC Struct Biol. 2009 Jun 10;9:40. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-9-40. BMC Struct Biol. 2009. PMID: 19515238 Free PMC article.
-
SUPFAM--a database of potential protein superfamily relationships derived by comparing sequence-based and structure-based families: implications for structural genomics and function annotation in genomes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):289-93. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.1.289. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 11752317 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of Deinococcus radiodurans tunicamycin-resistance protein (TmrD), a phosphotransferase.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2008 Jun 1;64(Pt 6):479-86. doi: 10.1107/S1744309108011822. Epub 2008 May 16. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2008. PMID: 18540055 Free PMC article.
-
High resolution crystal structure of Sco5413, a widespread actinomycete MarR family transcriptional regulator of unknown function.Proteins. 2013 Jan;81(1):176-82. doi: 10.1002/prot.24197. Epub 2012 Nov 5. Proteins. 2013. PMID: 23042442
-
Domain of unknown function (DUF) proteins in plants: function and perspective.Protoplasma. 2024 May;261(3):397-410. doi: 10.1007/s00709-023-01917-8. Epub 2023 Dec 30. Protoplasma. 2024. PMID: 38158398 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

