Graph theoretical analysis of complex networks in the brain
- PMID: 17908336
- PMCID: PMC1976403
- DOI: 10.1186/1753-4631-1-3
Graph theoretical analysis of complex networks in the brain
Abstract
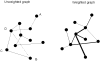
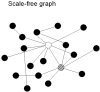
Since the discovery of small-world and scale-free networks the study of complex systems from a network perspective has taken an enormous flight. In recent years many important properties of complex networks have been delineated. In particular, significant progress has been made in understanding the relationship between the structural properties of networks and the nature of dynamics taking place on these networks. For instance, the 'synchronizability' of complex networks of coupled oscillators can be determined by graph spectral analysis. These developments in the theory of complex networks have inspired new applications in the field of neuroscience. Graph analysis has been used in the study of models of neural networks, anatomical connectivity, and functional connectivity based upon fMRI, EEG and MEG. These studies suggest that the human brain can be modelled as a complex network, and may have a small-world structure both at the level of anatomical as well as functional connectivity. This small-world structure is hypothesized to reflect an optimal situation associated with rapid synchronization and information transfer, minimal wiring costs, as well as a balance between local processing and global integration. The topological structure of functional networks is probably restrained by genetic and anatomical factors, but can be modified during tasks. There is also increasing evidence that various types of brain disease such as Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia, brain tumours and epilepsy may be associated with deviations of the functional network topology from the optimal small-world pattern.
Figures

References
-
- Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell ThM. Principles of neural science. McGraw-Hill; 2000.
-
- Le van Quyen M. Disentangling the dynamic core: a research program for a neurodynamics at the large scale. Biol Res. 2003;36:67–88. - PubMed
-
- Amaral LAN, Ottino JM. Complex networks. Augmenting the framework for the study of complex systems. Eur Phys J B. 2004;38:147–162. doi: 10.1140/epjb/e2004-00110-5. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

