Effect of protein source and resistance training on body composition and sex hormones
- PMID: 17908338
- PMCID: PMC1997115
- DOI: 10.1186/1550-2783-4-4
Effect of protein source and resistance training on body composition and sex hormones
Abstract
Background: Evidence suggests an inverse relationship between soy protein intake and serum concentrations of male sex hormones. Anecdotal evidence indicates that these alterations in serum sex hormones may attenuate changes in lean body mass following resistance training. However, little empirical data exists regarding the effects of soy and milk-based proteins on circulating androgens and exercise induced body composition changes.
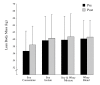
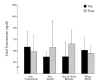
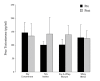
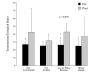
Methods: For 12 weeks 20 subjects were supplemented with 50 g per day of one of four different protein sources (Soy concentrate; Soy isolate; Soy isolate and whey blend, and Whey blend only) in combination with a resistance-training program. Body composition, testosterone, estradiol and sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) were measured at baseline and week 12.
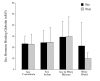
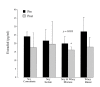
Results: Protein supplementation resulted in a significant increase in lean body mass independent of protein source (0.5 +/- 1.1 and 0.9 +/- 1.4 kg, p = 0.006, p = 0.007). No significant differences were observed between groups for total and free testosterone, SHBG, percentage body fat, BMI or body weight. The Testosterone/Estradiol ratio increased across all groups (+13.4, p = 0.005) and estradiol decreased (p = 0.002). Within group analysis showed significant increases in the Testosterone/Estradiol ratio in soy isolate + whey blend group (+16.3, p = 0.030). Estradiol was significantly lower in the whey blend group (-9.1 +/- 8.7 pg/ml, p = 0.033).
Conclusion: This investigation shows that 12 week supplementation with soy protein does not decrease serum testosterone or inhibit lean body mass changes in subjects engaged in a resistance exercise program.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effects of soy and whey protein supplementation on acute hormonal reponses to resistance exercise in men.J Am Coll Nutr. 2013;32(1):66-74. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2013.770648. J Am Coll Nutr. 2013. PMID: 24015701 Clinical Trial.
-
Whey protein supplementation during resistance training augments lean body mass.J Am Coll Nutr. 2013;32(2):122-35. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2013.793580. J Am Coll Nutr. 2013. PMID: 24015719 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of daily 24-gram doses of rice or whey protein on resistance training adaptations in trained males.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2020 Dec 1;17(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12970-020-00394-1. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2020. PMID: 33261645 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Determinants of sex hormone-binding globulin blood concentrations in premenopausal and postmenopausal women with different estrogen status. Virgilio-Menopause-Health Group.Metabolism. 1997 Jan;46(1):5-9. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(97)90159-1. Metabolism. 1997. PMID: 9005961
-
Exercise type and fat mass loss regulate breast cancer-related sex hormones in obese and overweight postmenopausal women.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2020 Jun;120(6):1277-1287. doi: 10.1007/s00421-020-04361-1. Epub 2020 Apr 7. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32266494 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Resistance training with soy vs whey protein supplements in hyperlipidemic males.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2009 Mar 11;6:8. doi: 10.1186/1550-2783-6-8. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2009. PMID: 19284589 Free PMC article.
-
ISSN exercise & sports nutrition review update: research & recommendations.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2018 Aug 1;15(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12970-018-0242-y. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2018. PMID: 30068354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
No Significant Differences in Muscle Growth and Strength Development When Consuming Soy and Whey Protein Supplements Matched for Leucine Following a 12 Week Resistance Training Program in Men and Women: A Randomized Trial.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 May 29;17(11):3871. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17113871. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32486007 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of protein/essential amino acids and resistance training on skeletal muscle hypertrophy: A case for whey protein.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2010 Jun 17;7:51. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-7-51. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2010. PMID: 20565767 Free PMC article.
-
Protein supplementation intake for bodybuilding and resistance training may impact sperm quality of subfertile men undergoing fertility treatment: a pilot study.Asian J Androl. 2019 Mar-Apr;21(2):208-211. doi: 10.4103/aja.aja_49_18. Asian J Androl. 2019. PMID: 30226218 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Gaudichon C, Mahe S, Benamouzig R, Luengo C, Fouillet H, Dare S, Van Oycke M, Ferriere F, Rautureau J, Tome D. Net postprandial utilization of [15N]-labeled milk protein nitrogen is influenced by diet composition in humans. J Nutr. 1999;129:890–895. - PubMed
-
- Makela S, Poutanen M, Kostian ML, Lehtimaki N, Strauss L, Santti R, Vihko R. Inhibition of 17beta-hydroxysteroid oxidoreductase by flavonoids in breast and prostate cancer cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1998;217:310–316. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
