Diabetic larvae and obese flies-emerging studies of metabolism in Drosophila
- PMID: 17908555
- PMCID: PMC2231808
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2007.09.002
Diabetic larvae and obese flies-emerging studies of metabolism in Drosophila
Abstract
The past few years have seen a shift in the use of Drosophila, from studies of growth and development toward genetic characterization of carbohydrate, sterol, and lipid metabolism. This research, reviewed below, establishes a new foundation for using this simple genetic model system to define the basic regulatory mechanisms that underlie metabolic homeostasis and holds the promise of providing new insights into the causes and treatments of critical human disorders such as diabetes and obesity.
Figures
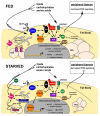
References
-
- Aguila JR, Suszko J, Gibbs AG, Hoshizaki DK. The role of larval fat cells in adult Drosophila melanogaster. The Journal of experimental biology. 2007;210:956–963. - PubMed
-
- Bier E. Drosophila, the golden bug, emerges as a tool for human genetics. Nature reviews. 2005;6:9–23. - PubMed
-
- Bohni R, Riesgo-Escovar J, Oldham S, Brogiolo W, Stocker H, Andruss BF, Beckingham K, Hafen E. Autonomous control of cell and organ size by CHICO, a Drosophila homolog of vertebrate IRS1-4. Cell. 1999;97:865–875. - PubMed
-
- Britton JS, Lockwood WK, Li L, Cohen SM, Edgar BA. Drosophila's insulin/PI3-kinase pathway coordinates cellular metabolism with nutritional conditions. Developmental cell. 2002;2:239–249. - PubMed
-
- Brogiolo W, Stocker H, Ikeya T, Rintelen F, Fernandez R, Hafen E. An evolutionarily conserved function of the Drosophila insulin receptor and insulin-like peptides in growth control. Curr Biol. 2001;11:213–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

