Tissue- and nuclear receptor-specific function of the C-terminal LXXLL motif of coactivator NCoA6/AIB3 in mice
- PMID: 17908797
- PMCID: PMC2169164
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00451-07
Tissue- and nuclear receptor-specific function of the C-terminal LXXLL motif of coactivator NCoA6/AIB3 in mice
Abstract
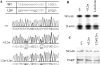
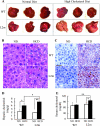
Although the LXXLL motif of nuclear receptor (NR) coactivators is essential for interaction with NRs, its role has not been assessed in unbiased animal models. The nuclear receptor coactivator 6 (NCoA6; also AIB3, PRIP, ASC-2, TRBP, RAP250, or NRC) is a coactivator containing an N-terminal LXXLL-1 (L1) and a C-terminal L2. L1 interacts with many NRs, while L2 interacts with the liver X receptor alpha (LXRalpha) and the estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha). We generated mice in which L2 was mutated into AXXAL (L2m) to disrupt its interaction with LXRalpha and ERalpha. NCoA6(L2m/L2m) mice exhibited normal reproduction, mammary gland morphogenesis, and ERalpha target gene expression. In contrast, when treated with an LXRalpha agonist, lipogenesis and the LXRalpha target gene expression were significantly reduced in NCoA6(L2m/L2m) mice. The induction of Cyp7A1 expression by a high-cholesterol diet was impaired in NCoA6(L2m/L2m) mice, which reduced bile acid synthesis in the liver and excretion in the feces and resulted in cholesterol accumulation in the liver and blood. These results demonstrate that L2 plays a tissue- and NR-specific role: it is required for NCoA6 to mediate LXRalpha-regulated lipogenesis and cholesterol/bile acid homeostasis in the liver but not required for ERalpha function in the mammary gland.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Nuclear receptor coactivator 6 mediates the synergistic activation of human cytochrome P-450 2C9 by the constitutive androstane receptor and hepatic nuclear factor-4alpha.Mol Pharmacol. 2008 Sep;74(3):913-23. doi: 10.1124/mol.108.048983. Epub 2008 Jun 13. Mol Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18552123 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear receptor coactivator/coregulator NCoA6(NRC) is a pleiotropic coregulator involved in transcription, cell survival, growth and development.Nucl Recept Signal. 2008 Feb 1;6:e002. doi: 10.1621/nrs.06002. Nucl Recept Signal. 2008. PMID: 18301782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activating signal cointegrator 2 required for liver lipid metabolism mediated by liver X receptors in mice.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 May;23(10):3583-92. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.10.3583-3592.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12724417 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription coactivator PRIP, the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-interacting protein, is redundant for the function of nuclear receptors PParalpha and CAR, the constitutive androstane receptor, in mouse liver.Gene Expr. 2007;13(4-5):255-69. doi: 10.3727/000000006780666948. Gene Expr. 2007. PMID: 17605299 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cholesterol-7alpha-hydroxylase: BAREly missing a SHP.J Lipid Res. 2002 Apr;43(4):533-43. J Lipid Res. 2002. PMID: 11907135 Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear receptors and epigenetic regulation: opportunities for nutritional targeting and disease prevention.Adv Nutr. 2014 Jul 14;5(4):373-85. doi: 10.3945/an.114.005868. Print 2014 Jul. Adv Nutr. 2014. PMID: 25022987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear receptor coactivator 6 mediates the synergistic activation of human cytochrome P-450 2C9 by the constitutive androstane receptor and hepatic nuclear factor-4alpha.Mol Pharmacol. 2008 Sep;74(3):913-23. doi: 10.1124/mol.108.048983. Epub 2008 Jun 13. Mol Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18552123 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of ASC-2 as an antiatherogenic transcriptional coactivator of liver X receptors in macrophages.Mol Endocrinol. 2009 Jul;23(7):966-74. doi: 10.1210/me.2008-0308. Epub 2009 Apr 2. Mol Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19342446 Free PMC article.
-
A tumor suppressive coactivator complex of p53 containing ASC-2 and histone H3-lysine-4 methyltransferase MLL3 or its paralogue MLL4.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 May 26;106(21):8513-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0902873106. Epub 2009 May 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19433796 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Flightless-I as a substrate of the cytokine-independent survival kinase CISK.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 22;284(21):14377-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M807770200. Epub 2009 Mar 17. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19293151 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albers, M., B. Blume, T. Schlueter, M. B. Wright, I. Kober, C. Kremoser, U. Deuschle, and M. Koegl. 2006. A novel principle for partial agonism of liver X receptor ligands. Competitive recruitment of activators and repressors. J. Biol. Chem. 281:4920-4930. - PubMed
-
- Caira, F., P. Antonson, M. Pelto-Huikko, E. Treuter, and J. A. Gustafsson. 2000. Cloning and characterization of RAP250, a novel nuclear receptor coactivator. J. Biol. Chem. 275:5308-5317. - PubMed
-
- Chiang, J. Y. 2002. Bile acid regulation of gene expression: roles of nuclear hormone receptors. Endocr. Rev. 23:443-463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
