Light and electron microscopy characteristics of the muscle of patients with SURF1 gene mutations associated with Leigh disease
- PMID: 17908801
- PMCID: PMC2571978
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2007.051060
Light and electron microscopy characteristics of the muscle of patients with SURF1 gene mutations associated with Leigh disease
Abstract
Aims: Leigh syndrome (LS) is characterised by almost identical brain changes despite considerable causal heterogeneity. SURF1 gene mutations are among the most frequent causes of LS. Although deficiency of cytochrome c oxidase (COX) is a typical feature of the muscle in SURF1-deficient LS, other abnormalities have been rarely described. The aim of the present work is to assess the skeletal muscle morphology coexisting with SURF1 mutations from our own research and in the literature.
Methods: Muscle samples from 21 patients who fulfilled the criteria of LS and SURF1 mutations (14 homozygotes and 7 heterozygotes of c.841delCT) were examined by light and electron microscopy.
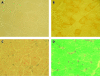
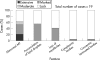
Results: Diffuse decreased activity or total deficit of COX was revealed histochemically in all examined muscles. No ragged red fibres (RRFs) were seen. Lipid accumulation and fibre size variability were found in 14 and 9 specimens, respectively. Ultrastructural assessment showed several mitochondrial abnormalities, lipid deposits, myofibrillar disorganisation and other minor changes. In five cases no ultrastructural changes were found. Apart from slight correlation between lipid accumulation shown by histochemical and ultrastructural techniques, no other correlations were revealed between parameters investigated, especially between severity of morphological changes and the patient's age at the biopsy.
Conclusion: Histological and histochemical features of muscle of genetically homogenous SURF1-deficient LS were reproducible in detection of COX deficit. Minor muscle changes were not commonly present. Also, ultrastructural abnormalities were not a consistent feature. It should be emphasised that SURF1-deficient muscle assessed in the light and electron microscopy panel may be interpreted as normal if COX staining is not employed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical and magnetic resonance imaging findings in patients with Leigh syndrome and SURF1 mutations.Brain Dev. 2014 Oct;36(9):807-12. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2013.10.012. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Brain Dev. 2014. PMID: 24262866
-
Unusual clinical presentations in four cases of Leigh disease, cytochrome C oxidase deficiency, and SURF1 gene mutations.J Child Neurol. 2005 Aug;20(8):670-4. doi: 10.1177/08830738050200080701. J Child Neurol. 2005. PMID: 16225813
-
Cytochrome C oxydase deficiency: SURF1 gene investigation in patients with Leigh syndrome.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Mar 18;497(4):1043-1048. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.169. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29481804
-
[Cytochrome c oxidase deficiency--SURF1 mutations].Nihon Rinsho. 2002 Apr;60 Suppl 4:446-9. Nihon Rinsho. 2002. PMID: 12013909 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Long survival in Leigh syndrome: new cases and review of literature.Neuropediatrics. 2014 Dec;45(6):346-53. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1383823. Epub 2014 Aug 11. Neuropediatrics. 2014. PMID: 25111564 Review.
Cited by
-
Serial cryoFIB/SEM Reveals Cytoarchitectural Disruptions in Leigh Syndrome Patient Cells.Structure. 2021 Jan 7;29(1):82-87.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2020.10.003. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Structure. 2021. PMID: 33096015 Free PMC article.
-
SURF1 related Leigh syndrome: Clinical and molecular findings of 16 patients from Turkey.Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2020 Oct 23;25:100657. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2020.100657. eCollection 2020 Dec. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2020. PMID: 33134083 Free PMC article.
-
Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC) and low mitochondrial membrane potential are specific for Barth syndrome.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2013 Nov;36(6):929-37. doi: 10.1007/s10545-013-9584-4. Epub 2013 Jan 30. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2013. PMID: 23361305 Free PMC article.
-
Motor neuron mitochondrial dysfunction in spinal muscular atrophy.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Aug 15;25(16):3395-3406. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw262. Epub 2016 Aug 3. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 27488123 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment of Leigh Syndrome Based on SURF1: Genotype and Phenotype.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Dec 5;10(12):1950. doi: 10.3390/antiox10121950. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943053 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Di Donato S. Disorders related to mitochondrial membranes: pathology of the respiratory chain and neurodegeneration. J Inherit Metab Dis 2000;23:247–63 - PubMed
-
- Zhu Z, Yao J, Johns T, et al. SURF1, encoding a factor involved in the biogenesis of cytochrome c oxidase, is mutated in Leigh syndrome. Nat Genet 1998;20:337–43 - PubMed
-
- Tirani V, Jaksch M, Hofmann S, et al. Loss-of-function mutations of SURF-1 are specifically associated with Leigh syndrome with cytochrome c oxidase deficiency. Ann Neurol 1999;46:161–6 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
