Chlamydia trachomatis species-specific induction of ezrin tyrosine phosphorylation functions in pathogen entry
- PMID: 17908813
- PMCID: PMC2168331
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01096-07
Chlamydia trachomatis species-specific induction of ezrin tyrosine phosphorylation functions in pathogen entry
Abstract
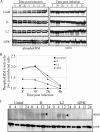
Chlamydia trachomatis is an obligate intracellular pathogen of humans that exhibits species-specific biological characteristics in its early interactions with host cells that are likely important to pathogenesis. One such characteristic is the tyrosine phosphorylation (Tyr-P) of an approximately 70-kDa polypeptide that occurs only after infection of mammalian cells by human strains. We sought to identify this protein because of its potential significance to the pathogenesis of human chlamydial infections. Using an immunoproteomic approach we identified the host protein ezrin, a member of the ezrin-radixin-moesin (ERM) protein family that serves as a physical link between host cell receptors and the actin cytoskeleton. Confocal microscopy studies showed colocalization of ezrin and actin at the tips and crypts of microvilli, the site of chlamydial attachment and entry, respectively. To demonstrate a functional role for ezrin we infected cells with a dominant-negative (DN) ezrin phenotype or treated cells with ezrin-specific small interfering RNA (siRNA). We found that both DN and siRNA-treated cells were significantly less susceptible to infection by human chlamydial strains. Moreover, we demonstrated that inhibition of infection in ezrin DN cells occurred at the stage of chlamydial entry. We hypothesize that the C. trachomatis-specific Tyr-P of ezrin might relate to an undefined species-specific mechanism of pathogen entry that involves chlamydial specific ligand(s) and host cell coreceptor usage.
Figures



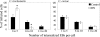

References
-
- Birkelund, S., L. Bini, V. Pallini, M. Sanchez-Campillo, S. Liberatori, J. D. Clausen, S. Ostergaard, A. Holm, and G. Christiansen. 1997. Characterization of Chlamydia trachomatis L2-induced tyrosine-phosphorylated HeLa cell proteins by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 18:563-567. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

