A comprehensive ChIP-chip analysis of E2F1, E2F4, and E2F6 in normal and tumor cells reveals interchangeable roles of E2F family members
- PMID: 17908821
- PMCID: PMC2045138
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.6783507
A comprehensive ChIP-chip analysis of E2F1, E2F4, and E2F6 in normal and tumor cells reveals interchangeable roles of E2F family members
Abstract
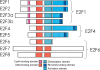
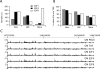
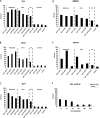
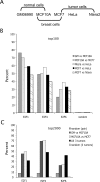
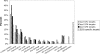
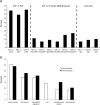
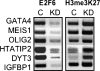
Using ChIP-chip assays (employing ENCODE arrays and core promoter arrays), we examined the binding patterns of three members of the E2F family in five cell types. We determined that most E2F1, E2F4, and E2F6 binding sites are located within 2 kb of a transcription start site, in both normal and tumor cells. In fact, the majority of promoters that are active (as defined by TAF1 or POLR2A binding) in GM06990 B lymphocytes and Ntera2 carcinoma cells were also bound by an E2F. This very close relationship between E2F binding sites and binding sites for general transcription factors in both normal and tumor cells suggests that a chromatin-bound E2F may be a signpost for active transcription initiation complexes. In general, we found that several E2Fs bind to a given promoter and that there is only modest cell type specificity of the E2F family. Thus, it is difficult to assess the role of any particular E2F in transcriptional regulation, due to extreme redundancy of target promoters. However, Ntera2 carcinoma cells were exceptional in that a large set of promoters were bound by E2F6, but not by E2F1 or E2F4. It has been proposed that E2F6 contributes to gene silencing by recruiting enzymes involved in methylating histone H3. To test this hypothesis, we created Ntera2 cell lines harboring shRNAs to E2F6. We found that reduction of E2F6 only induced minimal alteration of the transcriptome of Ntera2 transcriptome. Our results support the concept of functional redundancy in the E2F family and suggest that E2F6 is not critical for histone methylation.
Figures
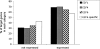
Similar articles
-
E2F-HDAC complexes negatively regulate the tumor suppressor gene ARHI in breast cancer.Oncogene. 2006 Jan 12;25(2):230-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209025. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 16158053
-
Activating E2Fs mediate transcriptional regulation of human E2F6 repressor.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006 Jan;290(1):C189-99. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00630.2004. Epub 2005 Aug 17. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16107498
-
E2F6 associates with BRG1 in transcriptional regulation.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47967. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047967. Epub 2012 Oct 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23082233 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing roles of E2Fs in cell proliferation and death.Cancer Biol Ther. 2004 Dec;3(12):1208-11. doi: 10.4161/cbt.3.12.1494. Epub 2004 Dec 21. Cancer Biol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15662116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo genome-wide binding of Id2 to E2F4 target genes as part of a reversible program in mice liver.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Sep;71(18):3583-97. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1588-1. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24573694 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tissue-specific direct targets of Caenorhabditis elegans Rb/E2F dictate distinct somatic and germline programs.Genome Biol. 2013 Jan 23;14(1):R5. doi: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-1-r5. Genome Biol. 2013. PMID: 23347407 Free PMC article.
-
E2F7 represses a network of oscillating cell cycle genes to control S-phase progression.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Apr;40(8):3511-23. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1203. Epub 2011 Dec 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22180533 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for autoregulation and cell signaling pathway regulation from genome-wide binding of the Drosophila retinoblastoma protein.G3 (Bethesda). 2012 Nov;2(11):1459-72. doi: 10.1534/g3.112.004424. Epub 2012 Nov 1. G3 (Bethesda). 2012. PMID: 23173097 Free PMC article.
-
Human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein associates with E2F6.J Virol. 2008 Sep;82(17):8695-705. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00579-08. Epub 2008 Jun 25. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18579589 Free PMC article.
-
The p107/E2F pathway regulates fibroblast growth factor 2 responsiveness in neural precursor cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Sep;29(17):4701-13. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01767-08. Epub 2009 Jun 29. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19564414 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Attwooll C., Oddi S., Cartwright P., Prosperini E., Agger K., Steensgaard P., Wagener C., Sardet C., Moroni M.C., Helin K., Oddi S., Cartwright P., Prosperini E., Agger K., Steensgaard P., Wagener C., Sardet C., Moroni M.C., Helin K., Cartwright P., Prosperini E., Agger K., Steensgaard P., Wagener C., Sardet C., Moroni M.C., Helin K., Prosperini E., Agger K., Steensgaard P., Wagener C., Sardet C., Moroni M.C., Helin K., Agger K., Steensgaard P., Wagener C., Sardet C., Moroni M.C., Helin K., Steensgaard P., Wagener C., Sardet C., Moroni M.C., Helin K., Wagener C., Sardet C., Moroni M.C., Helin K., Sardet C., Moroni M.C., Helin K., Moroni M.C., Helin K., Helin K. A novel repressive E2F6 complex containing the polycomb group protein, EPC1, that interacts with EZH2 in a proliferation- specific manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:1199–1208. - PubMed
-
- Bailey T.L., Gribskov M., Gribskov M. Score distributions for simultaneous matching to multiple motifs. J. Comput. Biol. 1997;4:45–59. - PubMed
-
- Bieda M., Xu X., Singer M., Green R., Farnham P.J., Xu X., Singer M., Green R., Farnham P.J., Singer M., Green R., Farnham P.J., Green R., Farnham P.J., Farnham P.J. Unbiased location analysis of E2F1 binding sites suggests a widespread role for E2F1 in the human genome. Genome Res. 2006;16:595–605. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carroll J.S., Liu X.S., Brodsky A.S., Li W., Meyer C.A., Szary A.J., Eeckhoute J., Shao W., Hestermann E.V., Geistlinger T.R., Liu X.S., Brodsky A.S., Li W., Meyer C.A., Szary A.J., Eeckhoute J., Shao W., Hestermann E.V., Geistlinger T.R., Brodsky A.S., Li W., Meyer C.A., Szary A.J., Eeckhoute J., Shao W., Hestermann E.V., Geistlinger T.R., Li W., Meyer C.A., Szary A.J., Eeckhoute J., Shao W., Hestermann E.V., Geistlinger T.R., Meyer C.A., Szary A.J., Eeckhoute J., Shao W., Hestermann E.V., Geistlinger T.R., Szary A.J., Eeckhoute J., Shao W., Hestermann E.V., Geistlinger T.R., Eeckhoute J., Shao W., Hestermann E.V., Geistlinger T.R., Shao W., Hestermann E.V., Geistlinger T.R., Hestermann E.V., Geistlinger T.R., Geistlinger T.R., et al. Chromosome-wide mapping of estrogen receptor binding reveals long-range regulation requiring the forkhead protein FoxA1. Cell. 2005;122:33–43. - PubMed
-
- Cartwright P., Muller H., Wagener C., Holm K., Helin K., Muller H., Wagener C., Holm K., Helin K., Wagener C., Holm K., Helin K., Holm K., Helin K., Helin K. E2F-6: A novel member of the E2F family is an inhibitor of E2F-dependent transcription. Oncogene. 1998;17:611–623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
