SMK-1/PPH-4.1-mediated silencing of the CHK-1 response to DNA damage in early C. elegans embryos
- PMID: 17908915
- PMCID: PMC2064732
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200705182
SMK-1/PPH-4.1-mediated silencing of the CHK-1 response to DNA damage in early C. elegans embryos
Erratum in
- J Cell Biol. 2009 Feb 23;184(4):613
Retraction in
-
Retraction. SMK-1/PPH-4.1-mediated silencing of the CHK-1 response to DNA damage in early C. elegans embryos.J Cell Biol. 2010 Jun 28;189(7):1187. doi: 10.1083/jcb.20070518206112010r. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20584918 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
During early embryogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans, the ATL-1-CHK-1 (ataxia telangiectasia mutated and Rad3 related-Chk1) checkpoint controls the timing of cell division in the future germ line, or P lineage, of the animal. Activation of the CHK-1 pathway by its canonical stimulus DNA damage is actively suppressed in early embryos so that P lineage cell divisions may occur on schedule. We recently found that the rad-2 mutation alleviates this checkpoint silent DNA damage response and, by doing so, causes damage-dependent delays in early embryonic cell cycle progression and subsequent lethality. In this study, we report that mutations in the smk-1 gene cause the rad-2 phenotype. SMK-1 is a regulatory subunit of the PPH-4.1 (protein phosphatase 4) protein phosphatase, and we show that SMK-1 recruits PPH-4.1 to replicating chromatin, where it silences the CHK-1 response to DNA damage. These results identify the SMK-1-PPH-4.1 complex as a critical regulator of the CHK-1 pathway in a developmentally relevant context.
Figures

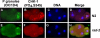
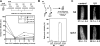




Similar articles
-
Checkpoint silencing during the DNA damage response in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos.J Cell Biol. 2006 Mar 27;172(7):999-1008. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200512136. Epub 2006 Mar 20. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16549501 Free PMC article.
-
chk-1 is an essential gene and is required for an S-M checkpoint during early embryogenesis.Cell Cycle. 2004 Sep;3(9):1196-200. Epub 2004 Sep 1. Cell Cycle. 2004. PMID: 15326393
-
Differential activation of the DNA replication checkpoint contributes to asynchrony of cell division in C. elegans embryos.Curr Biol. 2003 May 13;13(10):819-27. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00295-1. Curr Biol. 2003. PMID: 12747829
-
C. elegans epigenetic regulation in development and aging.Brief Funct Genomics. 2014 May;13(3):223-34. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elt048. Epub 2013 Dec 10. Brief Funct Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24326118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Checkpoint Kinase 1 Is a Key Signal Transducer of DNA Damage in the Early Mammalian Cleavage Embryo.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 5;24(7):6778. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076778. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047751 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A PP4 phosphatase complex dephosphorylates RPA2 to facilitate DNA repair via homologous recombination.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010 Mar;17(3):365-72. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1769. Epub 2010 Feb 14. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20154705 Free PMC article.
-
The role of protein phosphatase 4 in regulating microtubule severing in the Caenorhabditis elegans embryo.Genetics. 2009 Mar;181(3):933-43. doi: 10.1534/genetics.108.096016. Epub 2008 Dec 15. Genetics. 2009. PMID: 19087961 Free PMC article.
-
DAF-16 and SMK-1 Contribute to Innate Immunity During Adulthood in Caenorhabditis elegans.G3 (Bethesda). 2020 May 4;10(5):1521-1539. doi: 10.1534/g3.120.401166. G3 (Bethesda). 2020. PMID: 32161087 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin reassembly signals the end of DNA repair.Cell Cycle. 2008 Dec 15;7(24):3792-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.24.7188. Epub 2008 Dec 13. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 19066448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PP4 dephosphorylates Maf1 to couple multiple stress conditions to RNA polymerase III repression.EMBO J. 2012 Mar 21;31(6):1440-52. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.501. Epub 2012 Feb 14. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22333918 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoki, H., S. Sato, T. Takanami, T. Ishihara, I. Katsura, H. Takahashi, and A. Higashitani. 2000. Characterization of Ce-atl-1, an ATM-like gene from Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol. Gen. Genet. 264:119–126. - PubMed
-
- Bartek, J., C. Lukas, and J. Lukas. 2004. Checking on DNA damage in S phase. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5:792–804. - PubMed
-
- Brauchle, M., K. Baumer, and P. Gonczy. 2003. Differential activation of the DNA replication checkpoint contributes to asynchrony of cell division in C. elegans embryos. Curr. Biol. 13:819–827. - PubMed
-
- Conn, C.W., A.L. Lewellyn, and J.L. Maller. 2004. The DNA damage checkpoint in embryonic cell cycles is dependent on the DNA-to-cytoplasmic ratio. Dev. Cell. 7:275–281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

