A MurF inhibitor that disrupts cell wall biosynthesis in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 17908943
- PMCID: PMC2167990
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00845-07
A MurF inhibitor that disrupts cell wall biosynthesis in Escherichia coli
Abstract
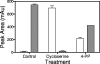
MurF is an essential enzyme of bacterial cell wall biosynthesis. Few MurF inhibitors have been reported, and none have displayed measurable antibacterial activity. Through the use of a MurF binding assay, a series of 8-hydroxyquinolines that bound to the Escherichia coli enzyme and inhibited its activity was identified. To derive additional chemotypes lacking 8-hydroxyquinoline, a known chelating moiety, a pharmacophore model was constructed from the series and used to select compounds for testing in the MurF binding and enzymatic inhibition assays. Whereas the original diverse library yielded 0.01% positive compounds in the binding assay, of which 6% inhibited MurF enzymatic activity, the pharmacophore-selected set yielded 14% positive compounds, of which 37% inhibited the enzyme, suggesting that the model enriched for compounds with affinity to MurF. A 4-phenylpiperidine (4-PP) derivative identified by this process displayed antibacterial activity (MIC of 8 microg/ml against permeable E. coli) including cell lysis and a 5-log(10)-unit decrease in CFU. Importantly, treatment of E. coli with 4-PP resulted in a 15-fold increase in the amount of the MurF UDP-MurNAc-tripeptide substrate, and a 50% reduction in the amount of the MurF UDP-MurNAc-pentapeptide product, consistent with inhibition of the MurF enzyme within bacterial cells. Thus, 4-PP is the first reported inhibitor of the MurF enzyme that may contribute to antibacterial activity by interfering with cell wall biosynthesis.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson, M. S., S. S. Eveland, H. R. Onishi, and D. L. Pompliano. 1996. Kinetic mechanism of the Escherichia coli UDPMurNAc-tripeptide d-alanyl-d-alanine-adding enzyme: use of a glutathione S-transferase fusion. Biochemistry 35:16264-16269. - PubMed
-
- Clement, O. O., and A. T. Mehl. 1999. HipHop: pharmacophores based on multiple common-feature alignments, p. 69-84. In O. F. Guner (ed.), Pharmacophore perception, development, and use in drug design. International University Line, La Jolla, CA.
-
- Crespo-Carbone, S. M., A. Klinger, Y. Wang, B. Foleno, E. Wira, K. Bush, and E. Z. Baum. 2005. ThermoFluor-based identification of inhibitors of MurF, an essential bacterial cell wall synthesis enzyme. Abstr. 45th Intersci. Conf. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., abstr. F-1849.
-
- Crespo-Carbone, S. M., I. Turchi, B. Foleno, Y. Kong, E. Wira, M. Macielag, K. Bush, and E. Z. Baum. 2006. A MurF inhibitor which disrupts biosynthesis of the bacterial cell wall. Abstr. 46th Intersci. Conf. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., abstr. F2-1171.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

