Epidermal growth factor receptor cooperates with signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer cells via up-regulation of TWIST gene expression
- PMID: 17909010
- PMCID: PMC2570961
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0575
Epidermal growth factor receptor cooperates with signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer cells via up-regulation of TWIST gene expression
Abstract
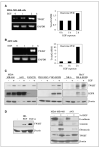
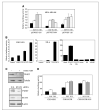
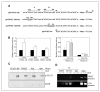
Aberrant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling is a major cause of tumor progression and metastasis; the underlying mechanisms, however, are not well understood. In particular, it remains elusive whether deregulated EGFR pathway is involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), an early event that occurs during metastasis of cancers of an epithelial origin. Here, we show that EGF induces EGFR-expressing cancer cells to undergo a transition from the epithelial to the spindle-like mesenchymal morphology. EGF reduced E-cadherin expression and increased that of mesenchymal proteins. In search of a downstream mediator that may account for EGF-induced EMT, we focused on transcription repressors of E-cadherin, TWIST, SLUG, and Snail and found that cancer cells express high levels of TWIST and that EGF enhances its expression. EGF significantly increases TWIST transcripts and protein in EGFR-expressing lines. Forced expression of EGFR reactivates TWIST expression in EGFR-null cells. TWIST expression is suppressed by EGFR and Janus-activated kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) inhibitors, but not significantly by those targeting phosphoinositide-3 kinase and MEK/ERK. Furthermore, constitutively active STAT3 significantly activates the TWIST promoter, whereas the JAK/STAT3 inhibitor and dominant-negative STAT3 suppressed TWIST promoter. Deletion/mutation studies further show that a 26-bp promoter region contains putative STAT3 elements required for the EGF-responsiveness of the TWIST promoter. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays further show that EGF induces binding of nuclear STAT3 to the TWIST promoter. Immunohistochemical analysis of 130 primary breast carcinomas indicates positive correlations between non-nuclear EGFR and TWIST and between phosphorylated STAT3 and TWIST. Together, we report here that EGF/EGFR signaling pathways induce cancer cell EMT via STAT3-mediated TWIST gene expression.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition promotes breast cancer progression via a fibronectin-dependent STAT3 signaling pathway.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 21;288(25):17954-67. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.475277. Epub 2013 May 7. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23653350 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 pathway up-regulates estrogen receptor-beta expression in lung adenocarcinoma cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2011 Jul;25(7):1145-58. doi: 10.1210/me.2010-0495. Epub 2011 May 5. Mol Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21546410 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of NF-κB by the RANKL/RANK system up-regulates snail and twist expressions and induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in mammary tumor cell lines.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Sep 5;32(1):62. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-32-62. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24011086 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Akt activity induces the mesenchymal-to-epithelial reverting transition with restoring E-cadherin expression in KB and KOSCC-25B oral squamous cell carcinoma cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Feb 26;28(1):28. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-28-28. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19243631 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive activation of STAT3 in breast cancer cells: A review.Int J Cancer. 2016 Jun 1;138(11):2570-8. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29923. Epub 2015 Nov 28. Int J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26559373 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment With Medicinal Mushroom Extract Mixture Inhibits Translation and Reprograms Metabolism in Advanced Colorectal Cancer Animal Model as Evidenced by Tandem Mass Tags Proteomics Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Aug 21;11:1202. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01202. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32973493 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotype switching in melanoma: implications for progression and therapy.Front Oncol. 2015 Feb 13;5:31. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2015.00031. eCollection 2015. Front Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25763355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stimulus-dependent differences in signalling regulate epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity and change the effects of drugs in breast cancer cell lines.Cell Commun Signal. 2015 May 15;13:26. doi: 10.1186/s12964-015-0106-x. Cell Commun Signal. 2015. PMID: 25975820 Free PMC article.
-
Heat stress induces epithelial plasticity and cell migration independent of heat shock factor 1.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2012 Nov;17(6):765-78. doi: 10.1007/s12192-012-0349-z. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2012. PMID: 22791010 Free PMC article.
-
RCP induces Slug expression and cancer cell invasion by stabilizing β1 integrin.Oncogene. 2017 Feb 23;36(8):1102-1111. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.277. Epub 2016 Aug 15. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 27524413
References
-
- Verbeek BS, Adriaansen-Slot SS, Vroom TM, Beckers T, Rijksen G. Overexpression of EGFR and c-erbB2 causes enhanced cell migration in human breast cancer cells and NIH3T3 fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1998;425:145–50. - PubMed
-
- Bruns CJ, Solorzano CC, Harbison MT, et al. Blockade of the epidermal growth factor receptor signaling by a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor leads to apoptosis of endothelial cells and therapy of human pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2000;60:2926–35. - PubMed
-
- Matsuo M, Sakurai H, Saiki I. ZD1839, a selective epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, shows antimetastatic activity using a hepatocellular carcinoma model. Mol Cancer Ther. 2003;2:557–61. - PubMed
-
- Weber KL, Doucet M, Price JE, et al. Blockade of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling leads to inhibition of renal cell carcinoma growth in the bone of nude mice. Cancer Res. 2003;63:2940–7. - PubMed
-
- Shintani S, Li C, Mihara M, Nakashiro K, Hamakawa H. Gefitinib (‘Iressa’), an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, mediates the inhibition of lymph node metastasis in oral cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2003;201:149–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

