New molecularly targeted therapies for lung cancer
- PMID: 17909619
- PMCID: PMC1994616
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI31809
New molecularly targeted therapies for lung cancer
Abstract
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death worldwide. The disease is particularly difficult to detect, and patients often present at an advanced stage. Current treatments have limited effectiveness, and unfortunately, the prognosis remains poor. Recent insights into the molecular pathogenesis and biologic behavior of lung cancer have led to the development of rationally designed methods of early detection, prevention, and treatment of this disease. This article will review the important clinical implications of these advances, with a focus on new molecularly targeted therapies currently in development.
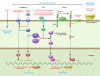
Figures

References
-
- Parkin D.M., Bray F., Ferlay J., Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Govindan R., et al. Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006;24:4539–4544. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A., et al. Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2006;56:106–130. - PubMed
-
- Graham E.A., Singer J.J. Landmark article Oct 28, 1933. Successful removal of an entire lung for carcinoma of the bronchus. By Evarts A. Graham and J.J. Singer. JAMA. 1984;251:257–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

