Why targeted therapy hasn't worked in advanced cancer
- PMID: 17909624
- PMCID: PMC1994633
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI33190
Why targeted therapy hasn't worked in advanced cancer
Abstract
In this issue of the JCI, Nissen et al. report that a reciprocal interaction exists between the growth factors FGF2 and PDGF-BB, causing tumors to exhibit increased angiogenesis and metastatic potential. Both FGF2 and PDGF-BB signal through tyrosine kinase receptors, which have been the target of tyrosine kinase inhibitors for cancer therapies. These inhibitors are usually small molecules that inhibit the kinase activity of a receptor or nonreceptor tyrosine kinase, preventing downstream signaling. The results of this study shed light on why tyrosine kinase inhibitors have been useful for the treatment of only a small number of advanced cancers. Currently, a major focus of pharmaceutical companies is to develop ever more potent and specific tyrosine kinases. The results presented here suggest that this approach may not be successful.
Figures
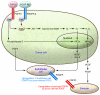
Comment on
-
Angiogenic factors FGF2 and PDGF-BB synergistically promote murine tumor neovascularization and metastasis.J Clin Invest. 2007 Oct;117(10):2766-77. doi: 10.1172/JCI32479. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17909625 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sawyers C.L., et al. Imatinib induces hematologic and cytogenetic responses in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in myeloid blast crisis: results of a phase II study. Blood. 2002;99:3530–9. - PubMed
-
- Hsieh R.K., Lim K.H., Kuo H.T., Tzen C.Y., Huang M.J. Female sex and bronchioloalveolar pathologic subtype predict EGFR mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Chest. 2005;128:317–321. - PubMed
-
- Yatabe Y., Kosaka T., Takahashi T., Mitsudomi T. EGFR mutation is specific for terminal respiratory unit type adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2005;29:633–639. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

