Macrophages suppress T cell responses and arthritis development in mice by producing reactive oxygen species
- PMID: 17909630
- PMCID: PMC1994618
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI31935
Macrophages suppress T cell responses and arthritis development in mice by producing reactive oxygen species
Abstract
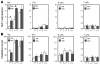
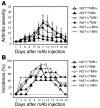
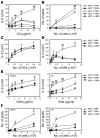
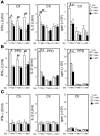
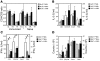
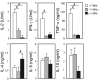
Reduced capacity to produce ROS increases the severity of T cell-dependent arthritis in both mice and rats with polymorphisms in neutrophil cytosolic factor 1 (Ncf1) (p47phox). Since T cells cannot exert oxidative burst, we hypothesized that T cell responsiveness is downregulated by ROS produced by APCs. Macrophages have the highest burst capacity among APCs, so to study the effect of macrophage ROS on T cell activation, we developed transgenic mice expressing functional Ncf1 restricted to macrophages. Macrophage-restricted expression of functional Ncf1 restored arthritis resistance to the level of that of wild-type mice in a collagen-induced arthritis model but not in a T cell-independent anti-collagen antibody-induced arthritis model. T cell activation was downregulated and skewed toward Th2 in transgenic mice. In vitro, IL-2 production and T cell proliferation were suppressed by macrophage ROS, irrespective of T cell origin. IFN-gamma production, however, was independent of macrophage ROS but dependent on T cell origin. These effects were antigen dependent but not restricted to collagen type II. In conclusion, macrophage-derived ROS play a role in T cell selection, maturation, and differentiation, and also a suppressive role in T cell activation, and thereby mediate protection against autoimmune diseases like arthritis.
Figures


References
-
- Feldmann M., Brennan F.M., Maini R.N. Rheumatoid arthritis. Cell. 1996;85:307–310. - PubMed
-
- MacGregor A.J., et al. Characterizing the quantitative genetic contribution to rheumatoid arthritis using data from twins. Arthritis Rheum. . 2000;43:30–37. - PubMed
-
- Johannesson M., Hultqvist M., Holmdahl R. Genetics of autoimmune diseases: a multistep process. Curr. Top. Microbiol.Immunol. 2006;305:259–276. - PubMed
-
- Olofsson P., Holmberg J., Tordsson J., Lu S., Akerstrom B., Holmdahl R. Positional identification of Ncf1 as a gene that regulates arthritis severity in rats. Nat. Genet. 2003;33:25–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

