Enhancement of dendritic cell-tumor fusion vaccine potency by indoleamine-pyrrole 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitor, 1-MT
- PMID: 17909857
- PMCID: PMC12161613
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-007-0315-9
Enhancement of dendritic cell-tumor fusion vaccine potency by indoleamine-pyrrole 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitor, 1-MT
Abstract
Purpose: Dendritic cell (DC)-based cancer vaccines are currently being evaluated as novel anti-tumor vaccination strategies, but in some cases, they are demonstrated to have poor clinical efficacies than anticipated. A potential reason is immune tolerance due to the immunosuppressive enzyme, indoleamine-pyrrole 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO). The aim of this study was to determine whether blocking the activity of IDO might improve the anti-tumor efficacy of DC/Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) fusion vaccine applied to the mouse LLC model.
Methods: To prepare the DC/LLC fusion vaccine, DCs were fused with LLC using polyethylene glycol (PEG) as described. The IDO expression in the DC/LLC fusion vaccine and in the vaccinated mice was detected by western blot (WB) and/or immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis. This fusion vaccine, as a single agent or in combination with 1-methyl-tryptophan (1-MT, an IDO inhibitor), was administered to LLC mice. The anti-tumor efficacy in different treatment was determined by regular observation of tumor development and the level of splenic cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) response, which was examined by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release.
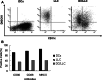
Results: In the LLC mice, we observed that IDO-positive cells were extensively accumulated in tumor draining lymph nodes (TDLNs). Furthermore, WB and IHC analysis results showed that vaccination with fusion DC/LLC cells alone caused significant up-regulation of IDO in spleens. 1-MT enhanced the anti-tumor efficacy elicited by DC/LLC fusion vaccine via delaying the tumor development and inducing stronger splenic CTL responses.
Conclusions: Our results indicate an IDO-mediated immunosuppressive mechanism might be involved in weakening the anti-tumor efficacy elicited by DC/LLC fusion vaccine, and specific inhibition of IDO activity might be required for development of cancer vaccines.
Figures



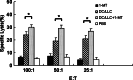
Similar articles
-
Astragaloside IV inhibits progression of lung cancer by mediating immune function of Tregs and CTLs by interfering with IDO.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014 Nov;140(11):1883-90. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1744-x. Epub 2014 Jul 1. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24980548 Free PMC article.
-
1-methyl-tryptophan improves anxiety-like behavior in colitis mice by inhibiting neuroinflammation, promoting cell regeneration, and decreasing apoptosis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2025 Jan 21;219(1):uxaf030. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxaf030. Clin Exp Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40355363
-
Nodal Expansion, Tumor Infiltration and Exhaustion of Neoepitope-Specific Th Cells After Prophylactic Peptide Vaccination and Anti-CTLA4 Therapy in Mouse Melanoma B16.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 4;26(13):6453. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136453. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650228 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity and seroefficacy of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Jul;28(34):1-109. doi: 10.3310/YWHA3079. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39046101 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy of Neoantigen-Loaded Dendritic Cell Vaccine Immunotherapy in Non-Metastatic Gastric Cancer.Med Sci (Basel). 2025 Jul 11;13(3):90. doi: 10.3390/medsci13030090. Med Sci (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40700119 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bacterial extracellular vesicles-based therapeutic strategies for bone and soft tissue tumors therapy.Theranostics. 2022 Sep 11;12(15):6576-6594. doi: 10.7150/thno.78034. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 36185613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity and clinical outcome following induction chemotherapy and concurrent chemoradiation in Stage III non-small cell lung cancer.Oncoimmunology. 2013 Mar 1;2(3):e23428. doi: 10.4161/onci.23428. Oncoimmunology. 2013. PMID: 23802083 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in nasopharyngeal carcinoma impairs the cytolytic function of peripheral blood lymphocytes.BMC Cancer. 2009 Nov 30;9:416. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-416. BMC Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19948041 Free PMC article.
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and dendritic cell tolerogenicity.Immunol Invest. 2012;41(6-7):738-64. doi: 10.3109/08820139.2012.676122. Immunol Invest. 2012. PMID: 23017144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase: is it an immune suppressor?Cancer J. 2010 Jul-Aug;16(4):354-9. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0b013e3181eb3343. Cancer J. 2010. PMID: 20693847 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Banchereau J, Steinman RM (1998) Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature 392:245–252 - PubMed
-
- Basu GD, Tinder TL, Bradley JM, Tu T, Hattrup CL, Pockaj BA, Mukherjee P (2006) Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor enhances the efficacy of a breast cancer vaccine: role of IDO. J Immunol 177:2391–2402 - PubMed
-
- Breckpot K, Heirman C, De Greef C, van der Bruggen P, Thielemans K (2004) Identification of new antigenic peptide presented by HLA-Cw7 and encoded by several MAGE genes using dendritic cells transduced with lentiviruses. J Immunol 172:2232–2237 - PubMed
-
- Chouaib S, Asselin PC, Mami CF, Caignard A, Blay JY (1997) The host-tumor immune conflict: from immunosuppression to resistance and destruction. Immunol Today 18:493–497 - PubMed
-
- Du J, Cai SH, Shi Z, Nagase F (2004) Binding activity of H-Ras is necessary for in vivo inhibition of ASK1 activity. Cell Res 14:148–154 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

