Role of echocardiography in diagnosis and risk stratification in heart failure with left ventricular systolic dysfunction
- PMID: 17910744
- PMCID: PMC2064911
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-7120-5-34
Role of echocardiography in diagnosis and risk stratification in heart failure with left ventricular systolic dysfunction
Abstract
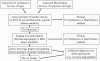
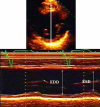
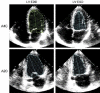
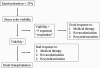
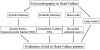
Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome that can result from any structural or functional cardiac disorder that impairs the ability of the ventricle to fill with or eject blood. Echocardiography represents the "gold standard" in the assessment of LV systolic dysfunction and in the recognition of systolic heart failure, since dilatation of the LV results in alteration of intracardiac geometry and hemodynamics leading to increased morbidity and mortality. The functional mitral regurgitation is a consequence of adverse LV remodelling that occurs with a structurally normal valve and it is a marker of adverse prognosis. Diastolic dysfunction plays a major role in signs and symptoms of HF and in the risk stratification, and provides prognostic information independently in HF patients and impaired systolic function. Ultrasound lung comets are a simple echographic sign of extravascular lung water, more frequently associated with left ventricular diastolic and/or systolic dysfunction, which can integrate the clinical and pathophysiological information provided by conventional echocardiography and provide a useful information for prognostic stratification of HF patients. Contractile reserve is defined as the difference between values of an index of left ventricular contractility during peak stress and its baseline values and the presence of myocardial viability predicts a favorable outcome. A non-invasive echocardiographic method for the evaluation of force-frequency relationship has been proposed to assess the changes in contractility during stress echo. In conclusion, in HF patients, the evaluation of systolic, diastolic function and myocardial contractile reserve plays a fundamental role in the risk stratification. The highest risk is present in HF patients with a heart that is weak, big, noisy, stiff and wet.
Figures


References
-
- Braunwald E. Heart disease. A textbook of cardiovascular medicine. 7. Sanduers; 2005.
-
- Remme WJ, McMurray JJ, Rauch B, Zannad F, Keukelaar K, Cohen-Solal A, Lopez-Sendon J, Hobbs FD, Grobbee DE, Boccanelli A, Cline C, Macarie C, Dietz R, Ruzyllo W. Public awareness of heart failure in Europe: first results from SHAPE. Eur Heart J. 2005;26:2413–2421. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehi447. - DOI - PubMed
-
- American Heart Association . Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics: 2005 Update. Dallas, Tex: American Heart Association; 2005.
-
- Hunt SA, Abraham WT, Chin MH, Feldman AM, Francis GS, Ganiats TG, Jessup M, Konstam MA, Mancini DM, Michl K, Oates JA, Rahko PS, Silver MA, Stevenson LW, Yancy CW. ACC/AHA 2005 guideline update for the diagnosis and management of chronic heart failure in the adult: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Update the 2001 Guidelines for the Evaluation and Management of Heart Failure) J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;46:e1–e82. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2005.08.023. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

