A pandemic strain of calicivirus threatens rabbit industries in the Americas
- PMID: 17910765
- PMCID: PMC2147015
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-4-96
A pandemic strain of calicivirus threatens rabbit industries in the Americas
Abstract
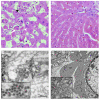
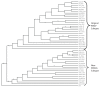
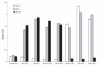
Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease (RHD) is a severe acute viral disease specifically affecting the European rabbit Oryctolagus cuniculus. As the European rabbit is the predominant species of domestic rabbit throughout the world, RHD contributes towards significant losses to rabbit farming industries and endangers wild populations of rabbits in Europe and other predatory animals in Europe that depend upon rabbits as a food source. Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease virus (RHDV) - a Lagovirus belonging to the family Caliciviridae is the etiological agent of RHD. Typically, RHD presents with sudden death in 70% to 95% of infected animals. There have been four separate incursions of RHDV in the USA, the most recent of which occurred in the state of Indiana in June of 2005. Animal inoculation studies confirmed the pathogenicity of the Indiana 2005 isolate, which caused acute death and pathological changes characterized by acute diffuse severe liver necrosis and pulmonary hemorrhages. Complete viral genome sequences of all USA outbreak isolates were determined and comparative genomics revealed that each outbreak was the result of a separate introduction of virus rather than from a single virus lineage. All of the USA isolates clustered with RHDV genomes from China, and phylogenetic analysis of the major capsid protein (VP60) revealed that they were related to a pandemic antigenic variant strain known as RHDVa. Rapid spread of the RHDVa pandemic suggests a selective advantage for this new subtype. Given its rapid spread, pathogenic nature, and potential to further evolve, possibly broadening its host range to include other genera native to the Americas, RHDVa should be regarded as a threat.
Figures
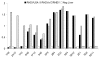


References
-
- Marcato PS, Benazzi C, Vecchi G, Galeotti M, Della Salda L, Sarli G, Lucidi P. Clinical and pathological features of viral haemorrhagic disease of rabbits and the European brown hare syndrome. Rev Sci Tech. 1991;10:371–392. - PubMed
-
- Capucci L, Scicluna MT, Lavazza A. Diagnosis of viral haemorrhagic disease of rabbits and the European brown hare syndrome. Rev Sci Tech. 1991;10:347–370. - PubMed
-
- Ferreira PG, Costa-e-Silva A, Monteiro E, Oliveira MJ, Aguas AP. Transient decrease in blood heterophils and sustained liver damage caused by calicivirus infection of young rabbits that are naturally resistant to rabbit haemorrhagic disease. Res Vet Sci. 2004;76:83–94. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2003.08.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arguello Villares JL. Viral haemorrhagic disease of rabbits: vaccination and immune response. Rev Sci Tech. 1991;10:459–480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

