Modulation of LMP1 protein expression by EBV-encoded microRNAs
- PMID: 17911266
- PMCID: PMC2042179
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0702896104
Modulation of LMP1 protein expression by EBV-encoded microRNAs
Abstract
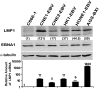
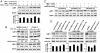
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) was the first human virus found to encode microRNAs (miRNAs), but the function of these miRNAs has been obscure. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is associated with EBV infection, and the EBV-encoded LMP1 is believed to be a key factor in NPC development. However, detection of LMP1 protein in NPC is variable. Here, we report that EBV-encoded BART miRNAs target the 3' UTR of the LMP1 gene and negatively regulate LMP1 protein expression. These miRNAs also modulate LMP1-induced NF-kappaB signaling and alleviate the cisplatin sensitivity of LMP1-expressing NPC cells. Consistent with a previous study on the NPC C666-1 cell line and C15 xenograft, we found abundant expression of BART miRNAs in NPC tissues. Furthermore, DNA sequencing revealed that the 3' UTR of LMP1 is highly conserved in NPC-derived EBV isolates. The data provide insight into the discrepancy between LMP1 transcript and protein detection in NPC and highlight the role of the EBV miRNAs in regulating LMP1 downstream signaling to promote cancer development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
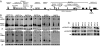


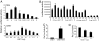
References
-
- Rickinson AB, Kieff E. In: Fields Virology. Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, editors. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001. pp. 2575–2625.
-
- Raab-Traub N. Semin Cancer Biol. 2002;12:431–441. - PubMed
-
- Kieff E, Rickinson AB. In: Fields Virology. Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, editors. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001. pp. 2511–2573.
-
- Young LS, Murray PG. Oncogene. 2003;22:5108–5121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

