ALK5- and TGFBR2-independent role of ALK1 in the pathogenesis of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia type 2
- PMID: 17911384
- PMCID: PMC2200847
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-08-107359
ALK5- and TGFBR2-independent role of ALK1 in the pathogenesis of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia type 2
Abstract
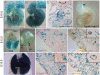
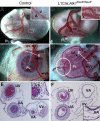
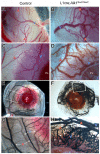
ALK1 belongs to the type I receptor family for transforming growth factor-beta family ligands. Heterozygous ALK1 mutations cause hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia type 2 (HHT2), a multisystemic vascular disorder. Based largely on in vitro studies, TGF-beta1 has been considered as the most likely ALK1 ligand related to HHT, yet the identity of the physiologic ALK1 ligand remains controversial. In cultured endothelial cells, ALK1 and another TGF-beta type I receptor, ALK5, regulate angiogenesis by controlling TGF-beta signal transduction, and ALK5 is required for ALK1 signaling. However, the extent to which such interactions between these 2 receptors play a role in pathogenesis of HHT is unknown. We directly addressed these issues in vivo by comparing the phenotypes of mice in which the Alk1, Alk5, or Tgfbr2 gene was conditionally deleted in restricted vascular endothelia using a novel endothelial Cre transgenic line. Alk1-conditional deletion resulted in severe vascular malformations mimicking all pathologic features of HHT. Yet Alk5- or Tgfbr2-conditional deletion in mice, or Alk5 inhibition in zebrafish, did not affect vessel morphogenesis. These data indicate that neither ALK5 nor TGFBR2 is required for ALK1 signaling pertinent to the pathogenesis of HHT and suggest that HHT might not be a TGF-beta subfamily disease.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, a vascular dysplasia affecting the TGF-beta signaling pathway.Clin Med Res. 2006 Mar;4(1):66-78. doi: 10.3121/cmr.4.1.66. Clin Med Res. 2006. PMID: 16595794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activin receptor-like kinase 1 modulates transforming growth factor-beta 1 signaling in the regulation of angiogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Mar 14;97(6):2626-31. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.6.2626. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10716993 Free PMC article.
-
Blood outgrowth endothelial cells from Hereditary Haemorrhagic Telangiectasia patients reveal abnormalities compatible with vascular lesions.Cardiovasc Res. 2005 Nov 1;68(2):235-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.06.009. Epub 2005 Jul 5. Cardiovasc Res. 2005. PMID: 15993872
-
Endoglin promotes endothelial cell proliferation and TGF-beta/ALK1 signal transduction.EMBO J. 2004 Oct 13;23(20):4018-28. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600386. Epub 2004 Sep 23. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15385967 Free PMC article.
-
ALK1 signaling in development and disease: new paradigms.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Dec;74(24):4539-4560. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2636-4. Epub 2017 Sep 4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28871312 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor is coordinately regulated by the activin-like kinase receptors 1 and 5 in endothelial cells.Blood. 2009 Sep 3;114(10):2197-206. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-01-199166. Epub 2009 Jun 8. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19506300 Free PMC article.
-
ALK1 as an emerging target for antiangiogenic therapy of cancer.Blood. 2011 Jun 30;117(26):6999-7006. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-01-330142. Epub 2011 Apr 5. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21467543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypertension overrides the protective effect of female hormones on the development of aortic aneurysm secondary to Alk5 deficiency via ERK activation.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Jan 15;308(2):H115-25. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00521.2014. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25398982 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia-associated Endoglin elicits hypoxia-driven heart failure in zebrafish.Dis Model Mech. 2023 May 1;16(5):dmm049488. doi: 10.1242/dmm.049488. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Dis Model Mech. 2023. PMID: 37264878 Free PMC article.
-
Nonischemic cerebral venous hypertension promotes a pro-angiogenic stage through HIF-1 downstream genes and leukocyte-derived MMP-9.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2009 Aug;29(8):1482-90. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2009.67. Epub 2009 May 27. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2009. PMID: 19471278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shovlin CL, Guttmacher AE, Buscarini E, et al. Diagnostic criteria for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome). Am J Med Genet. 2000;91:66–67. - PubMed
-
- McAllister KA, Grogg KM, Johnson DW, et al. Endoglin, a TGF-beta binding protein of endothelial cells, is the gene for hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia type 1. Nat Genet. 1994;8:345–351. - PubMed
-
- Johnson DW, Berg JN, Baldwin MA, et al. Mutations in the activin receptor-like kinase 1 gene in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia type 2. Nat Genet. 1996;13:189–195. - PubMed
-
- Seki T, Yun J, Oh SP. Arterial endothelium-specific activin receptor-like kinase 1 expression suggests its role in arterialization and vascular remodeling. Circ Res. 2003;93:682–689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

