Exacerbation of collagen-induced arthritis by oligoclonal, IL-17-producing gamma delta T cells
- PMID: 17911645
- PMCID: PMC2768546
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.8.5576
Exacerbation of collagen-induced arthritis by oligoclonal, IL-17-producing gamma delta T cells
Abstract
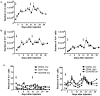
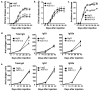
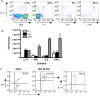
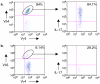
Murine gammadelta T cell subsets, defined by their Vgamma chain usage, have been shown in various disease models to have distinct functional roles. In this study, we examined the responses of the two main peripheral gammadelta T cell subsets, Vgamma1(+) and Vgamma4(+) cells, during collagen-induced arthritis (CIA), a mouse model that shares many hallmarks with human rheumatoid arthritis. We found that whereas both subsets increased in number, only the Vgamma4(+) cells became activated. Surprisingly, these Vgamma4(+) cells appeared to be Ag selected, based on preferential Vgamma4/Vdelta4 pairing and very limited TCR junctions. Furthermore, in both the draining lymph node and the joints, the vast majority of the Vgamma4/Vdelta4(+) cells produced IL-17, a cytokine that appears to be key in the development of CIA. In fact, the number of IL-17-producing Vgamma4(+) gammadelta T cells in the draining lymph nodes was found to be equivalent to the number of CD4(+)alphabeta(+) Th-17 cells. When mice were depleted of Vgamma4(+) cells, clinical disease scores were significantly reduced and the incidence of disease was lowered. A decrease in total IgG and IgG2a anti-collagen Abs was also seen. These results suggest that Vgamma4/Vdelta4(+) gammadelta T cells exacerbate CIA through their production of IL-17.
Figures
References
-
- Gregersen PK, Silver J, Winchester RJ. The shared epitope hypothesis. An approach to understanding the molecular genetics of susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1987;30:1205–13. - PubMed
-
- Wooley PH, Whalen JD, Chapdelaine JM. Collagen-induced arthritis in mice. VI. Synovial cells from collagen arthritic mice activate autologous lymphocytes in vitro. Cell Immunol. 1989;124:227–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

