Migration-promoting role of VEGF-C and VEGF-C binding receptors in human breast cancer cells
- PMID: 17912247
- PMCID: PMC2360449
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603993
Migration-promoting role of VEGF-C and VEGF-C binding receptors in human breast cancer cells
Abstract
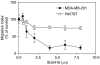
Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) is a lymphangiogenic factor over-expressed in highly metastatic, cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 expressing breast cancer cells. We tested the hypothesis that tumour-derived VEGF-C may play an autocrine role in metastasis by promoting cellular motility through one or more VEGF-C-binding receptors VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3, neuropilin (NRP)-1, NRP-2, and integrin alpha9beta1. We investigated the expression of these receptors in several breast cancer cell lines (MDA-MB-231, Hs578T, SK-BR-3, T-47D, and MCF7) and their possible requirement in migration of two VEGF-C-secreting, highly metastatic lines MDA-MB-231 and Hs578T. While cell lines varied significantly in their expression of above VEGF-C receptors, migratory activity of MDA-MB-231 and Hs578T cells was linked to one or more of these receptors. Depletion of endogenous VEGF-C by treatments with a neutralising antibody, VEGF-C siRNA or inhibitors of Src, EGFR/Her2/neu and p38 MAP kinases which inhibited VEGF-C production, inhibited cellular migration, indicating the requirement of VEGF-C for migratory function. Migration was differentially attenuated by blocking or downregulation of different VEGF-C receptors, for example treatment with a VEGFR-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, NRP-1 and NRP-2 siRNA or alpha9beta1 integrin antibody, indicating the participation of one or more of the receptors in cell motility. This novel role of tumour-derived VEGF-C indicates that breast cancer metastasis can be promoted by coordinated stimulation of lymphangiogenesis and enhanced migratory activity of breast cancer cells.
Figures




Similar articles
-
COX-2-mediated stimulation of the lymphangiogenic factor VEGF-C in human breast cancer.Br J Cancer. 2006 Apr 24;94(8):1154-63. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603067. Br J Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16570043 Free PMC article.
-
Co-expression of α9β1 integrin and VEGF-D confers lymphatic metastatic ability to a human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-468LN.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35094. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035094. Epub 2012 Apr 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22545097 Free PMC article.
-
VEGF/NRP-1axis promotes progression of breast cancer via enhancement of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and activation of NF-κB and β-catenin.Cancer Lett. 2016 Apr 1;373(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.01.010. Epub 2016 Jan 19. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 26805761
-
Roles of prostaglandins in tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis with special reference to breast cancer.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018 Sep;37(2-3):369-384. doi: 10.1007/s10555-018-9734-0. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018. PMID: 29858743 Review.
-
Autocrine functions of VEGF in breast tumor cells: adhesion, survival, migration and invasion.Cell Adh Migr. 2012 Nov-Dec;6(6):547-53. doi: 10.4161/cam.23332. Epub 2012 Nov 1. Cell Adh Migr. 2012. PMID: 23257828 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuropilin-2 expression in breast cancer: correlation with lymph node metastasis, poor prognosis, and regulation of CXCR4 expression.BMC Cancer. 2009 Jul 7;9:220. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-220. BMC Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19580679 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant therapy options in renal cell carcinoma - targeting the metastatic cascade.Nat Rev Urol. 2023 Mar;20(3):179-193. doi: 10.1038/s41585-022-00666-2. Epub 2022 Nov 11. Nat Rev Urol. 2023. PMID: 36369389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opposing Roles of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C in Metastatic Dissemination and Resistance to Radio/Chemotherapy: Discussion of Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2475:1-23. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2217-9_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35451746 Review.
-
Integrin alpha9beta1: Unique signaling pathways reveal diverse biological roles.Cell Adh Migr. 2010 Apr-Jun;4(2):194-8. doi: 10.4161/cam.4.2.10900. Epub 2010 Apr 8. Cell Adh Migr. 2010. PMID: 20179422 Free PMC article.
-
Phage-derived fully human monoclonal antibody fragments to human vascular endothelial growth factor-C block its interaction with VEGF receptor-2 and 3.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 2;5(8):e11941. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011941. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20689828 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bachelder RE, Lipscomb EA, Lin X, Wendt MA, Chadborn NH, Eickholt BJ, Mercurio AM (2003) Competing autocrine pathways involving alternative neuropilin-1 ligands regulate chemotaxis of carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 63: 5230–5233 - PubMed
-
- Bachelder RE, Wendt MA, Mercurio AM (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes breast carcinoma invasion in an autocrine manner by regulating the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Cancer Res 62: 7203–7206 - PubMed
-
- Basora N, Desloges N, Chang Q, Bouatrouss Y, Gosselin J, Poisson J, Sheppard D, Beaulieu JF (1998) Expression of the α9β1 integrin in human colonic epithelial cells: resurgence of the fetal phenotype in a subset of colon cancers and adenocarcinoma cell lines. Int J Cancer 75: 738–743 - PubMed
-
- Christensen C, Ambartsumian N, Gilestro G, Thomsen B, Comoglio P, Tamagnone L, Guldberg P, Lukanidin E (2005) Proteolytic processing converts the repelling signal Sema3E into an inducer of invasive growth and lung metastasis. Cancer Res 65: 6167–6177 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

