RNAi-mediated abrogation of cathepsin B and MMP-9 gene expression in a malignant meningioma cell line leads to decreased tumor growth, invasion and angiogenesis
- PMID: 17912429
- PMCID: PMC2031211
RNAi-mediated abrogation of cathepsin B and MMP-9 gene expression in a malignant meningioma cell line leads to decreased tumor growth, invasion and angiogenesis
Abstract
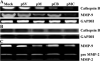
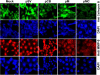
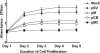
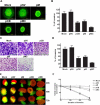
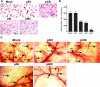
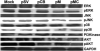
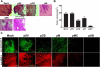
Malignant meningiomas are highly aggressive and frequently recur after surgical resection of the tumor. Earlier studies have reported that the cysteine protease cathepsin B and the matrix metalloproteinase MMP-9 play important roles in tumor progression. In the present study, we made an attempt to evaluate the roles of these proteases in the malignant meningioma tumor microenvironment and determined the effectiveness of using single or bicistronic siRNA constructs for cathepsin B and MMP-9, in both in vitro and in vivo models. Transfection of a plasmid vector expressing double-stranded RNA for cathepsin B and MMP-9 significantly inhibited mRNA and protein levels of cathepsin B and MMP-9. The migration and invasion of meningioma cells were decreased after treatment with single or bicistronic siRNA constructs for cathepsin B and MMP-9 compared to controls and vector controls. Inhibition of angiogenesis was observed when the cells were transfected with single or bicistronic constructs for cathepsin B and MMP-9, when compared to controls or empty vector controls. Our study revealed that abrogation of cathepsin B and MMP-9 expression decreased the activation of major proteins involved in MAP kinase and PI3 kinase pathways indicating that targeting these proteases may hinder intracellular signaling and thus decrease cell survival and proliferation in malignant meningiomas. In addition to the in vitro evidence, we observed a significant regression of pre-established orthotopic tumors after treatment with RNAi plasmid vectors targeting cathepsin B and MMP-9. Furthermore, these observations demonstrate that the simultaneous RNAi-mediated targeting of cathepsin B and MMP-9 has potential application for the treatment of human meningiomas.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RNA interference-mediated targeting of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor and matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene expression in the IOMM-lee malignant meningioma cell line inhibits tumor growth, tumor cell invasion and angiogenesis.Int J Oncol. 2007 Jul;31(1):5-17. Int J Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17549400 Free PMC article.
-
uPAR/cathepsin B overexpression reverse angiogenesis by rescuing FAK phosphorylation in uPAR/cathepsin B down regulated meningioma.PLoS One. 2011 Feb 11;6(2):e17123. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017123. PLoS One. 2011. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2020 Jan 29;15(1):e0228681. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228681. PMID: 21347260 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
uPA/uPAR downregulation inhibits radiation-induced migration, invasion and angiogenesis in IOMM-Lee meningioma cells and decreases tumor growth in vivo.Int J Oncol. 2008 Nov;33(5):937-47. Int J Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18949356 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of cathepsin B and MMP-9 gene expression in glioblastoma cell line via RNA interference reduces tumor cell invasion, tumor growth and angiogenesis.Oncogene. 2004 Jun 10;23(27):4681-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207616. Oncogene. 2004. Retraction in: Oncogene. 2025 Jun;44(20):1549. doi: 10.1038/s41388-025-03402-3. PMID: 15122332 Retracted.
-
Management of Atypical and Anaplastic Meningiomas.Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2016 Apr;27(2):239-47. doi: 10.1016/j.nec.2015.11.003. Epub 2016 Feb 20. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2016. PMID: 27012388 Review.
Cited by
-
Specialized roles for cysteine cathepsins in health and disease.J Clin Invest. 2010 Oct;120(10):3421-31. doi: 10.1172/JCI42918. Epub 2010 Oct 1. J Clin Invest. 2010. PMID: 20921628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smart Delivery Systems Responsive to Cathepsin B Activity for Cancer Treatment.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jun 29;15(7):1848. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071848. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37514035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shared Gene Expression and Immune Pathway Changes Associated with Progression from Nevi to Melanoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 21;14(1):3. doi: 10.3390/cancers14010003. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35008167 Free PMC article.
-
Cathepsin B is highly expressed in pancreatic cancer stem-like cells and is associated with patients' surgical outcomes.Oncol Lett. 2021 Jan;21(1):30. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12291. Epub 2020 Nov 11. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33240436 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular neuropathology of brain-invasive meningiomas.Brain Pathol. 2022 Mar;32(2):e13048. doi: 10.1111/bpa.13048. Brain Pathol. 2022. PMID: 35213084 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Erman T, Hanta I, Haciyakupoglu S, Zorludemir S, Zeren H, Gocer AI. Huge bilateral pulmonary and pleural metastasis from intracranial meningioma: a case report and review of the literature. J Neurooncol. 2005;74:179–181. - PubMed
-
- Clarke MR, Weyant RJ, Watson CG, Carty SE. Prognostic markers in pheochromocytoma. Hum Pathol. 1998;29:522–526. - PubMed
-
- DiCarlo A, Terracciano D, Mariano A, Macchia V. Urinary gelatinase activities (matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9) in human bladder tumors. Oncol Rep. 2006;15:1321–1326. - PubMed
-
- Guzinska-Ustymowicz K. MMP-9 and cathepsin B expression in tumor budding as an indicator of a more aggressive phenotype of colorectal cancer (CRC). Anticancer Res. 2006;26:1589–1594. - PubMed
-
- Naka T, Boltze C, Kuester D, Schulz TO, Samii A, Herold C, Ostertag H, Roessner A. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1, MMP-2, MMP-9, cathepsin B, and urokinase plasminogen activator in non-skull base chordoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 2004;122:926–930. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

