A refined radio-telemetry technique to monitor right ventricle or pulmonary artery pressures in rats: a useful tool in pulmonary hypertension research
- PMID: 17912547
- PMCID: PMC2137943
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-007-0334-z
A refined radio-telemetry technique to monitor right ventricle or pulmonary artery pressures in rats: a useful tool in pulmonary hypertension research
Abstract
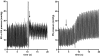
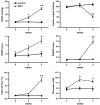
Implantable radio-telemetry methodology, allowing for continuous recording of pulmonary haemodynamics, has previously been used to assess effects of therapy on development and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. In the original procedure, rats were subjected to invasive thoracic surgery, which imposes significant stress that may disturb critical aspects of the cardiovascular system and delay recovery. In the present study, we describe and compare the original trans-thoracic approach with a new, simpler trans-diaphragm approach for catheter placement, which avoids the need for surgical invasion of the thorax. Satisfactory overall success rates up to 75% were achieved in both approaches, and right ventricular pressures and heart and respiratory rates normalised within 2 weeks. However, recovery was significantly faster in trans-diaphragm than in trans-thoracic operated animals (6.4+/-0.5 vs 9.5+/-1.1 days, respectively; p<0.05). Stable right ventricular pressures were recorded for more than 4 months, and pressure changes, induced by monocrotaline or pulmonary embolisms, were readily detected. The data demonstrate that right ventricular telemetry is a practicable procedure and a useful tool in pulmonary hypertension research in rats, especially when used in combination with echocardiography. We conclude that the described trans-diaphragm approach should be considered as the method of choice, for it is less invasive and simpler to perform.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Telemetry monitoring of pulmonary arterial pressure in freely moving rats.J Appl Physiol (1985). 1996 Aug;81(2):1027-32. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1996.81.2.1027. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1996. PMID: 8872676
-
Measurement of right ventricular pressure by telemetry in conscious moving rabbits.Lab Anim. 2013 Jul;47(3):175-183. doi: 10.1177/0023677213483725. Lab Anim. 2013. PMID: 23579323
-
Preserved right ventricular integrity in a new telemetric rat model of severe pulmonary hypertension.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017 Nov 1;313(5):L957-L963. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00278.2017. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28798258
-
Right Heart Catheterisation: How To Do It.Heart Lung Circ. 2019 Apr;28(4):e71-e78. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2018.08.005. Epub 2018 Sep 6. Heart Lung Circ. 2019. PMID: 30253970 Review.
-
The pulmonary artery catheter: a critical reappraisal.Cardiol Clin. 2013 Nov;31(4):545-65, viii. doi: 10.1016/j.ccl.2013.07.008. Cardiol Clin. 2013. PMID: 24188220 Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid quantification of myocardial fibrosis: a new macro-based automated analysis.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2011 Aug;34(4):343-54. doi: 10.1007/s13402-011-0035-7. Epub 2011 May 3. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2011. PMID: 21538025 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetic cardiomyopathy in Zucker diabetic fatty rats: the forgotten right ventricle.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2010 Jun 15;9:25. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-9-25. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2010. PMID: 20550678 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging the TGFβ type I receptor in pulmonary arterial hypertension.EJNMMI Res. 2023 Mar 22;13(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13550-023-00966-7. EJNMMI Res. 2023. PMID: 36947258 Free PMC article.
-
Nicorandil prevents right ventricular remodeling by inhibiting apoptosis and lowering pressure overload in rats with pulmonary arterial hypertension.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44485. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044485. Epub 2012 Sep 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22970229 Free PMC article.
-
A microsurgical technique for catheter insertion in the rat femoral artery.Acta Cir Bras. 2020 Nov 23;35(10):e202001004. doi: 10.1590/s0102-865020200100000004. eCollection 2020. Acta Cir Bras. 2020. PMID: 33237176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1378/chest.126.4.1313', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.126.4.1313'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15486398', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15486398/'}]}
- Chemla D, Castelain V, Humbert M, Hebert JL, Simonneau G, Lecarpentier Y, Herve P (2004) New formula for predicting mean pulmonary artery pressure using systolic pulmonary artery pressure. Chest 126:1313–1317 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15580021', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15580021/'}]}
- Gamblin TC, Wall CE Jr., Morgan JH III/, Erickson DJ, Dalton ML, Ashley DW (2004) The natural history of untreated penetrating diaphragm injury: an animal model. J Trauma 57:989–992 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/j.echo.2006.04.036', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.echo.2006.04.036'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17000367', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17000367/'}]}
- Hardziyenka M, Campian ME, de Bruin-Bon HA, Michel MC, Tan HL (2006) Sequence of echocardiographic changes during development of right ventricular failure in rat. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 19:1272–1279 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8872676', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8872676/'}]}
- Hess P, Clozel M, Clozel JP (1996) Telemetry monitoring of pulmonary arterial pressure in freely moving rats. J Appl Physiol 81:1027–1032 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1152/ajpheart.00369.2006', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00369.2006'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16731643', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16731643/'}]}
- Hessel MH, Steendijk P, den Adel B, Schutte CI, van der Laarse A (2006) Characterization of right ventricular function after monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in the intact rat. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291:H2424–H2430 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

